Onsite Experiment's Style feature lets you update several elements' properties.
Style
Using Style, you can:
Edit the fill color, which is the background color.
Upload a background image or select one from the image library.
Set the background image to be repeated.
The background image should be in the recommended size displayed on the Add Image prompt.
To edit the background color, click the Style button and select a color from the Fill option.
To upload a background image to the selected element, go to Style > Image and click the Upload button. When you add a background image, the fill color becomes invisible.
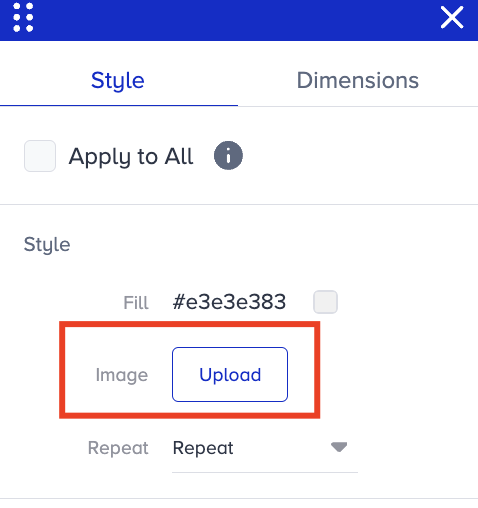
To control how the background image is displayed, go to Style > Repeat.
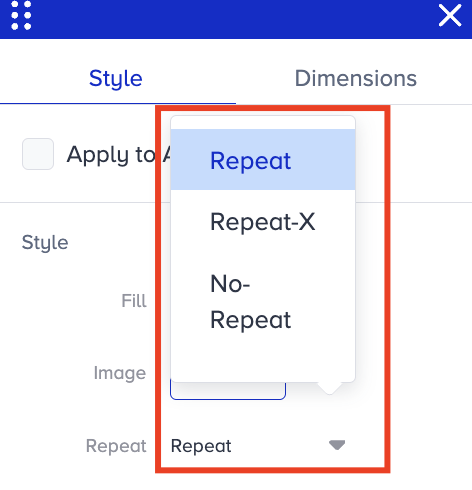
In the list below, you will find the repeat values and how they work:
Repeat: You can determine whether the background image repeats horizontally and vertically. When set to repeat, the image will be tiled horizontally and vertically to cover the entire background area of the element.
No Repeat: The background image will not repeat when set to no-repeat. It will be displayed only once, starting from the top-left corner of the element's background area, and will not stretch or tile to cover the entire area.
Repeat X: This is a shorthand for specifying that the background image should repeat horizontally only. It means that the image will repeat along the x-axis (horizontally) to cover the width of the background area, but will not repeat vertically.
Space: It behaves similarly to the repeat function, where the background image is repeated both horizontally and vertically. However, it adds spacing between the repeated images to distribute them evenly, avoiding partial images at the edges.
Round: It repeats the background image horizontally and vertically, adjusting the spacing between the repeated images to ensure even distribution. Any remaining space is filled with additional repetitions, ensuring that there is no partial image at the edges.
Initial: It sets the background image repetition behavior to its initial default value, as defined by the CSS specification. It resets any previously applied background image repetition settings to their default state.
Inherit: The background image repetition behavior should be inherited from the parent element. The current element's background image repeat property will be the same as that of its parent.
Text
You can update the following text properties:
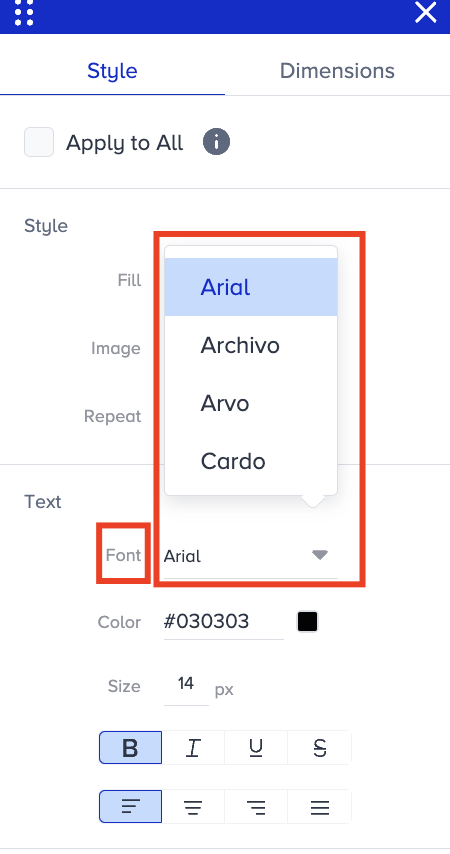
Font family
Text color
Font size
Font weight
Text decoration
Text alignment
Go to Text > Font to change the font of the selected text.
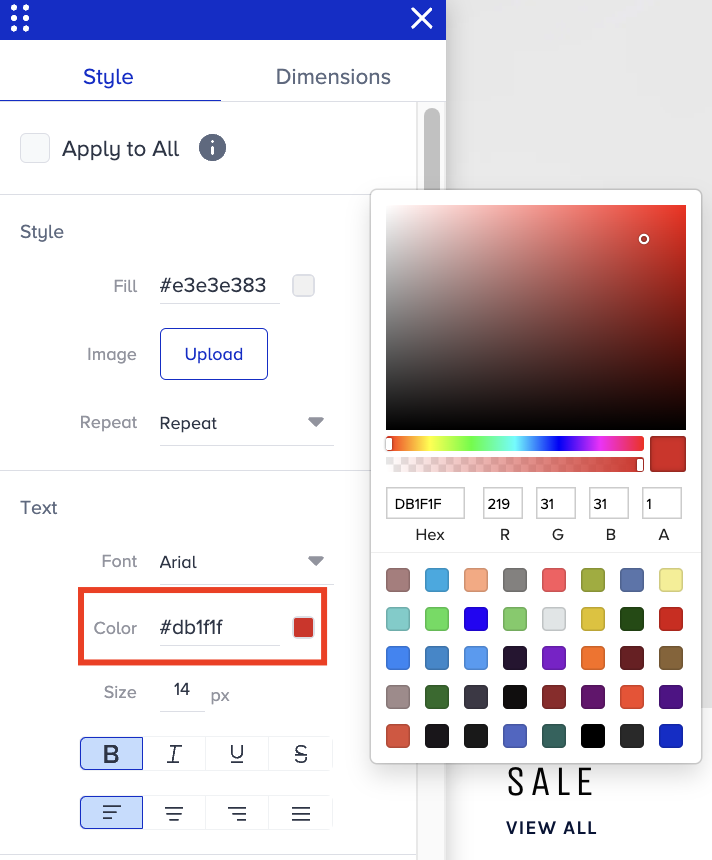
Go to Text > Color to change the text color.
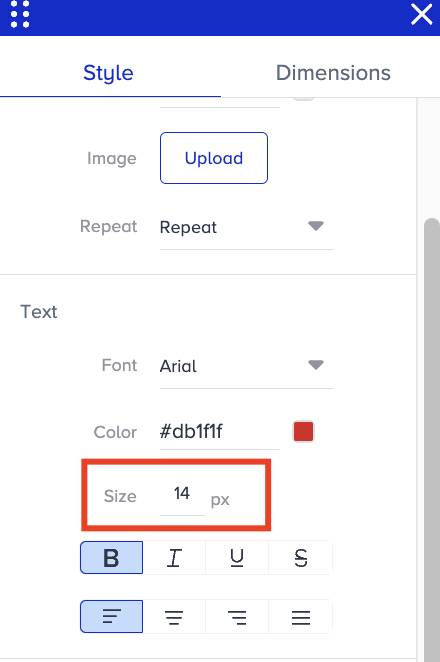
Go to Text > Size to change the font size of your text.
Border
Using Border, you can:
Add borders.
Style borders.
Change border color.
Add border-radius to have rounded corners.
Go to Settings to specify which side you want to apply the border to and by which pixel.
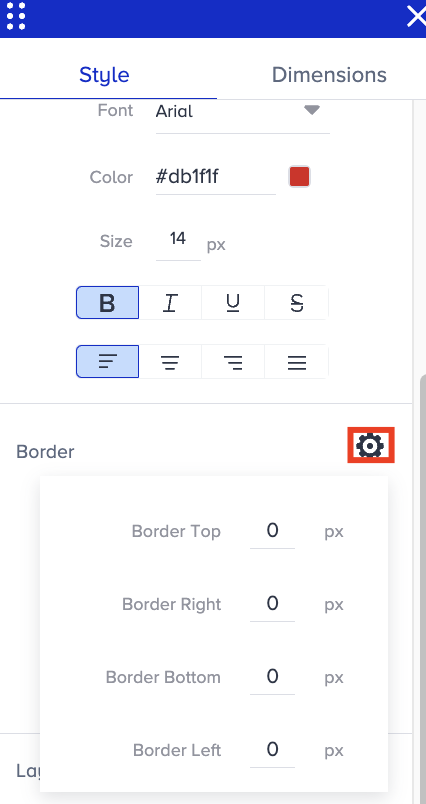
Go to Border > Style to change the style of an element's border.
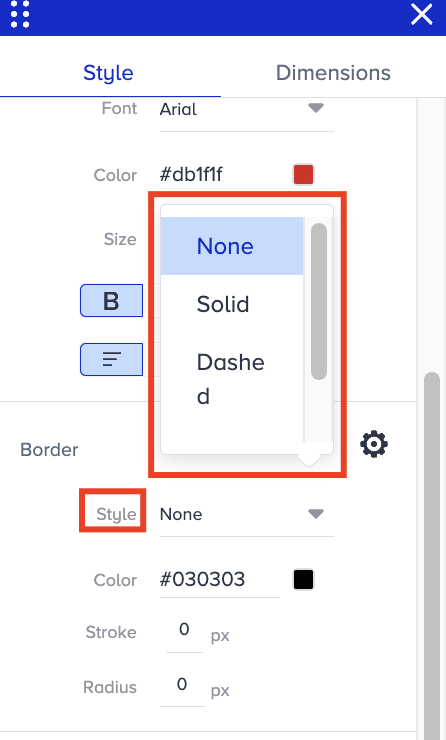
None: It removes the border altogether.
Solid: It creates a solid border.
Dashed: It creates a border with dashes.
Dotted: It creates a border with dots.
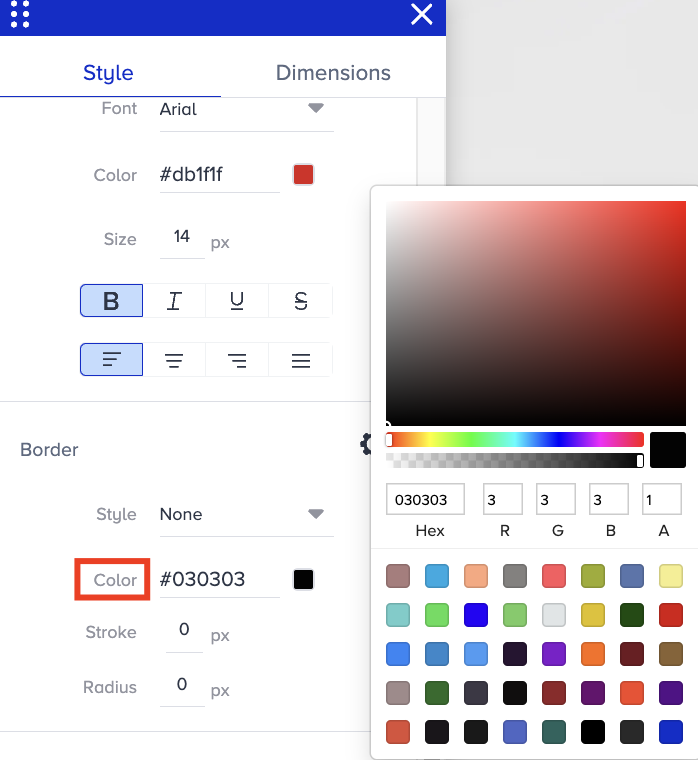
Go to Border > Color to change the border color of the selected element.
Go to Border > Stroke to change the thickness of the border style.
Go to Border > Radius to add rounded corners to the element's border.
Layout
The layout helps you remove any element or change its position. You can make changes to:
Z-index
Float
Display
Position attributes
.gif)
Go to Layout > Display to control how an element is displayed on your website. It determines the type of box generated for an element and how it behaves in the document flow.
Here are the Display values:
None: This value entirely hides the element from the layout, as if it doesn't exist in the document. The element will not appear on the page, and its space will be collapsed.
Inline: This value generates an inline-level box, meaning the element will flow with the surrounding content and only occupy as much width as necessary.
Block: This value generates an inline-level box as inline, but it allows you to set width, height, margins, and paddings like a block-level element. This is often used when you want an element to be part of the flow but have block-like properties.
Initial: It sets the element's display property to its default value.
Go to Layout > Position to change your website's positioning method for an element.
The Position values are:
Static: This is the default value. Elements with static positions are positioned according to the document's normal flow. The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have no effect.
Relative: Elements with relative positions are positioned relative to their normal position in the document flow. Setting the top, right, bottom, or left will move the element away from its normal position by the specified amount. Other elements are not affected by the element's positioning, and the space it occupied initially is still reserved for it.
Absolute: Elements with absolute position are removed from the normal document flow and relative to the nearest positioned ancestor (an ancestor with position: relative, absolute, or fixed position). If no positioned ancestor exists, it's positioned relative to the initial containing block (typically the <html> element). An absolutely positioned element can overlap other elements.
Fixed: Elements with fixed positions are removed from the normal document flow and positioned relative to the browser window. They remain fixed even when the page is scrolled. A common use case is for fixed headers or footers.
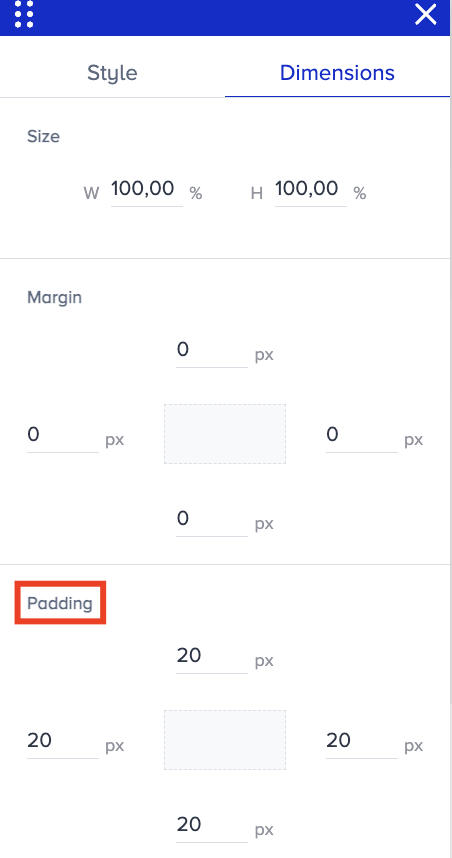
Dimensions
Dimensions help you change the following properties of an element:
Width & height
Margin
Padding
The value you see pre-filled corresponds to the element you are editing.
Go to Dimensions > Size to change the width and height of the selected element.
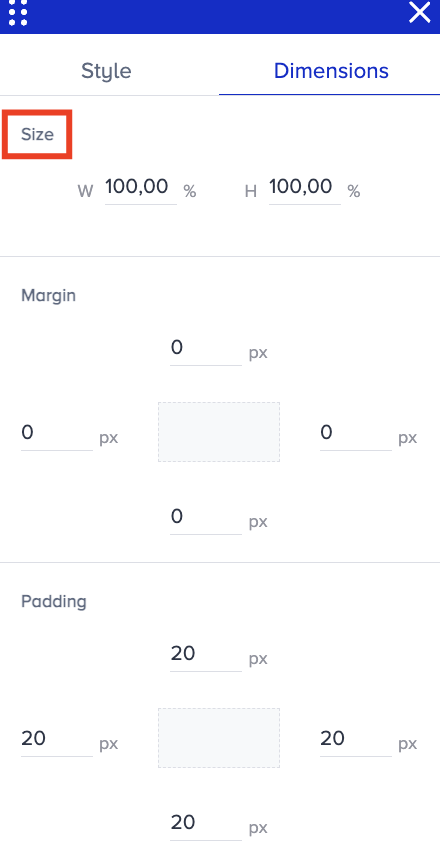
Go to Dimensions > Margin to control the spacing outside an element's border. It allows you to specify the amount of space that should be left around the element's outer edges.
.png)
Go to Dimensions > Padding to control the spacing between an element's content and border. It allows you to specify the amount of space left between the content and the border of an element.