Smart Recommender enhances your website’s product recommendations with advanced personalization and filtering techniques. By tailoring suggestions to user behavior, it ensures that customers see the most relevant products at the right time, improving engagement, boosting conversions, and creating a more optimized shopping experience.
Why personalization matters
Effective product recommendations don’t just increase sales, they also strengthen customer loyalty. Personalization ensures that:
Customers discover new products aligned with their preferences.
Irrelevant suggestions (e.g., already purchased or recently viewed items) are excluded.
Recommendations match user interests, leading to higher conversion rates and stronger retention.
Set up advanced personalization
Enhance recommendations with Attribute Affinity
Attribute Affinity segments users based on their interactions with specific product attributes and boosts items that match those preferences in recommendations. Enabling this feature ensures customers are shown more products they’re likely to engage with.
To enable Attribute Affinity:
Navigate to Product Catalog Management > Product Attributes.
Select the attributes to be used for Attribute Affinity calculations.
Enable the “Personalize recommendations based on attribute affinity” checkbox to prioritize products aligned with user preferences.

You can only select up to 5 product attributes for Attribute Affinity calculations.
Exclude specific products from recommendations
Exclusions help refine recommendations by preventing redundant or irrelevant product recommendations.
Exclude the Products in the Cart
Prevents showing products that the user has already added to their cart.
To enable this feature, enable the Exclude the Products in Cart checkbox in your strategy.
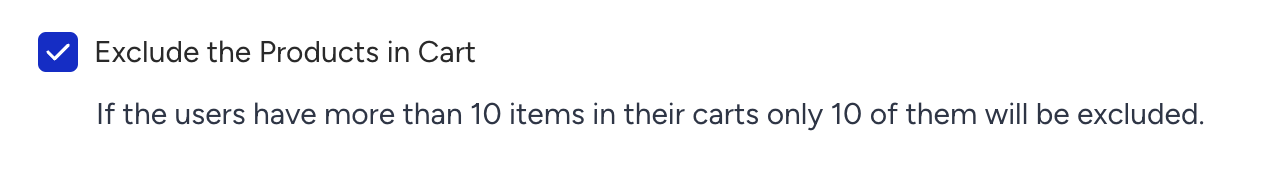
If the user’s cart contains more than 10 items, only the first 10 are excluded.
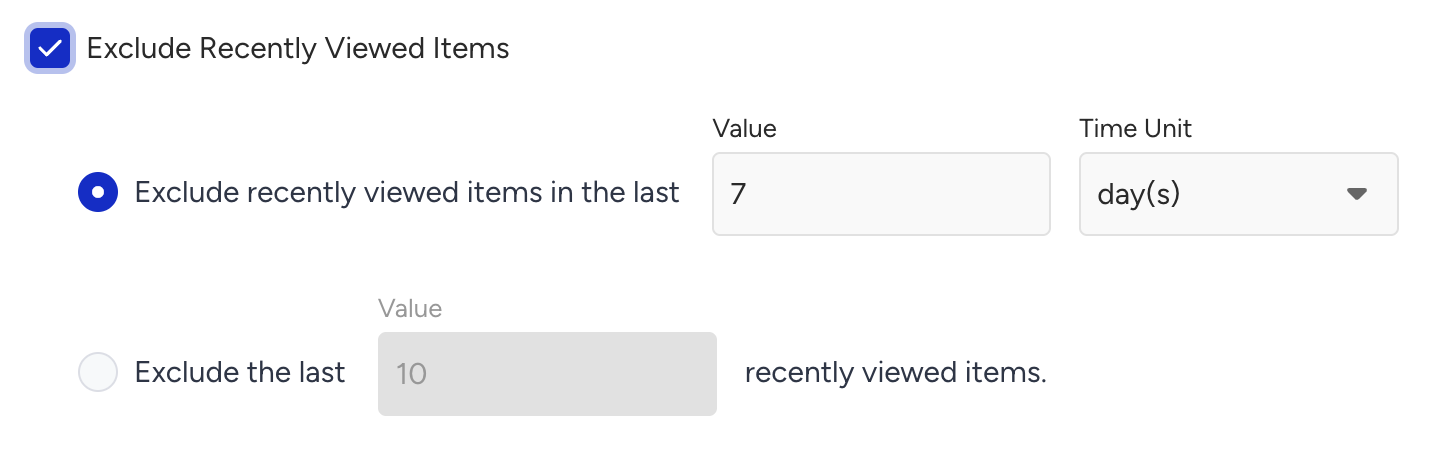
Exclude Recently Viewed Products
Avoids recommending products a user has already seen.
To enable the Exclude Recently Viewed Products feature, you can set either a look-back period or the number of the last viewed items to be excluded:
Look-back period: Exclusion of recently viewed products in a time period. The look-back period is configured as 1 - 30 days or 1 - 4 weeks and its default value is 7 days.
Last X viewed items: Exclusion of recently last X viewed products. The number of last X items can be configured in between 1 - 100 and its default value is 10.
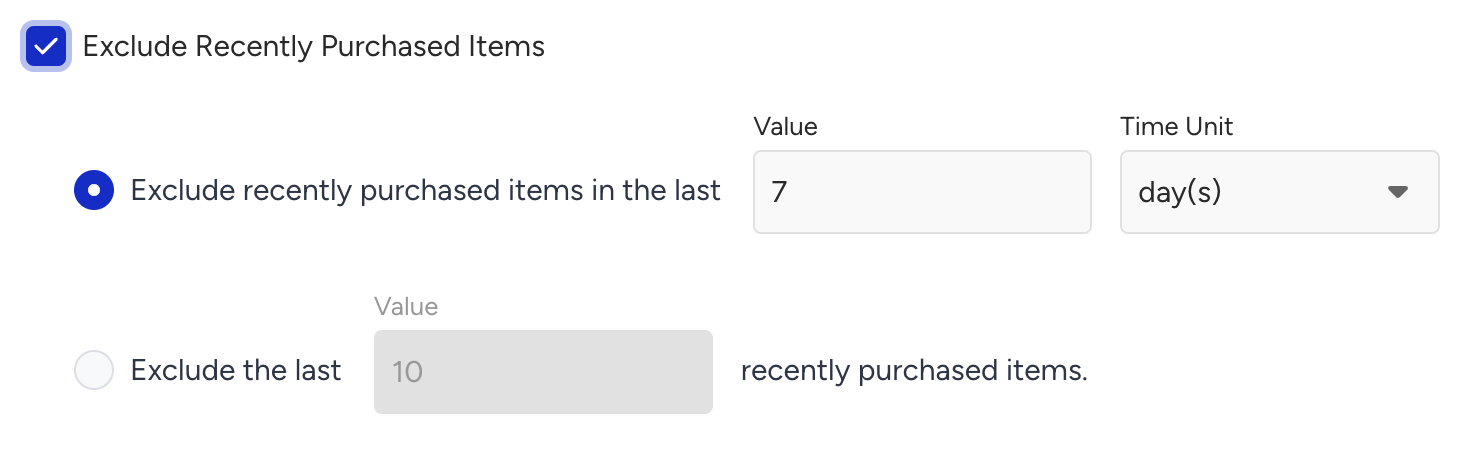
Exclude Recently Purchased Products
Prevents recommending items that a user has already bought.
To enable the Exclude Recently Purchased Products feature, you can set either a look-back period or the number of the last purchased items to be excluded:
Look-back period: Exclusion of recently purchased products in a time period. The look-back period is configured as 1 - 30 days or 1 - 4 weeks and its default value is 7 days.
Last X purchased items: Exclusion of recently last X purchased products. The number of last X items is configured as 1 - 100 and its default value is 10.
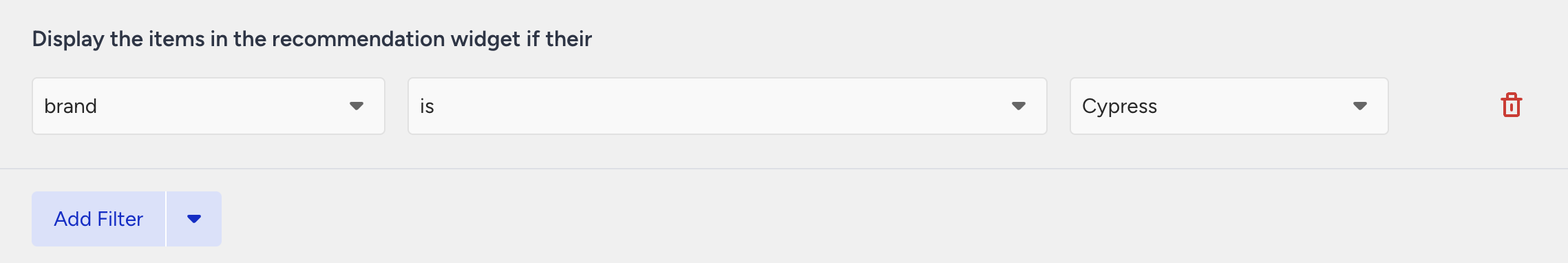
Use filters to customize recommendations
Filters refine recommendation results based on specific criteria. A filter consists of:
Attribute (e.g., category, brand, price)
Operator (e.g., is, contains, is one of, is more than)
Value (value of the selected attribute)
Apply a filter
Click the Add Filter button.
Select an attribute to filter by.
Choose an operator to define how the filter applies.
Set a value to refine the recommendation.
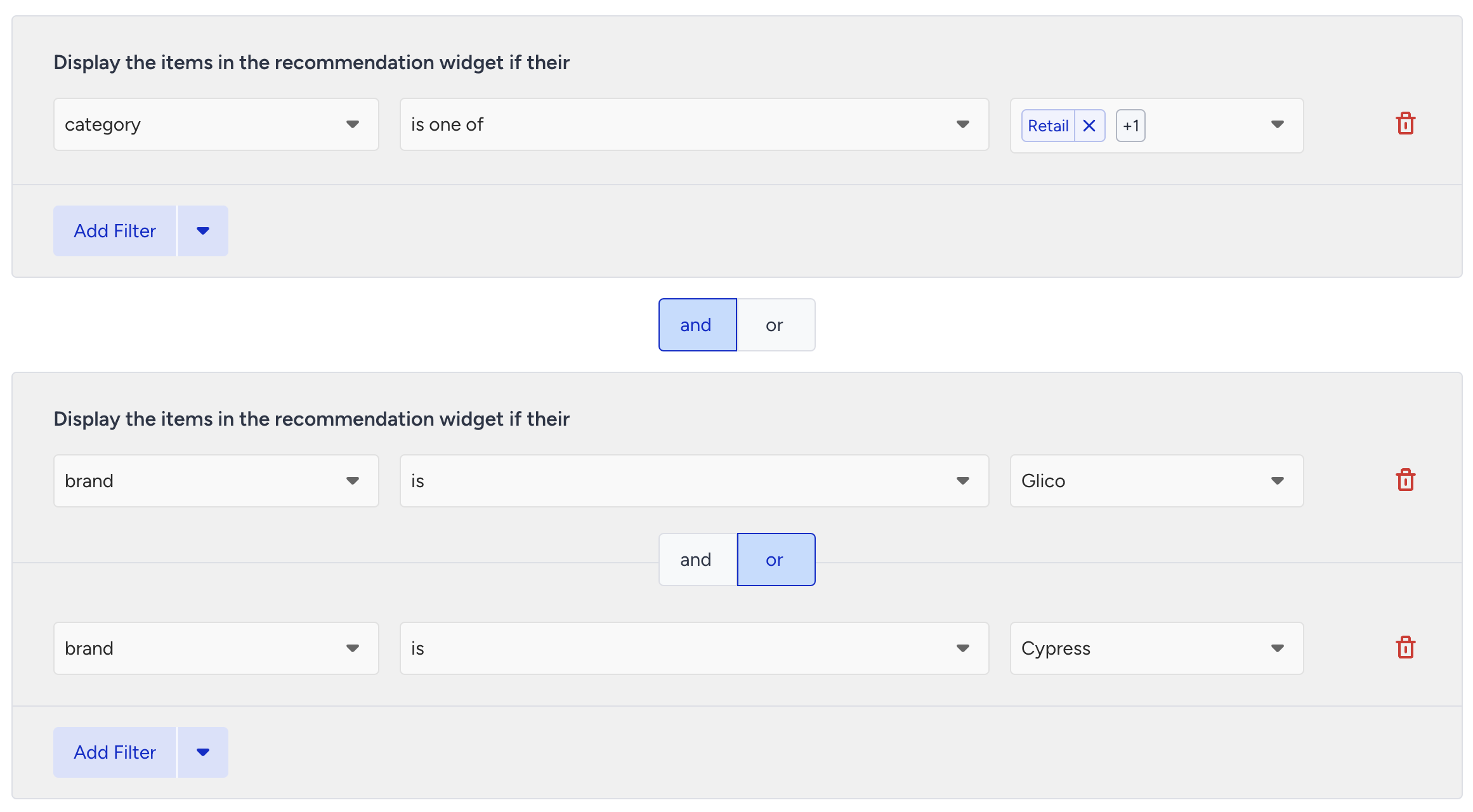
Filter groups
Filters can be combined using logical connectors:
AND: Products must meet all selected filter conditions.
OR: Products must meet at least one filter condition.
You can create multiple filter groups and connect them using AND/OR to customize recommendations further.
Dynamic values for real-time filtering
Operators like “matches the item they’re currently viewing” don’t require a value selection. This is because these operators dynamically filter the recommendations based on the product a user is currently viewing. Dynamic filters ensure that recommendations remain relevant by adapting to the user’s browsing context.
Two ways, which Insider One can retrieve the attribute’s value from a user’s viewing product in order to filter the products, are available:
System Rules: Dynamic values are obtained directly from the partner’s website through system rules. If the campaign is on a product page, getCurrentProduct() system rule is used to retrieve the attribute’s value. If the campaign is on a category page, getCategories() system rule is used to retrieve the category value.
Product ID Matching: Dynamic values are obtained based on the Product ID of the item a user is viewing. The necessary attribute value is derived from the product catalog using the Product ID collected from the user’s currently viewing product.
You can select the dynamic value source from the Product Catalog Management > Product Catalog Settings.
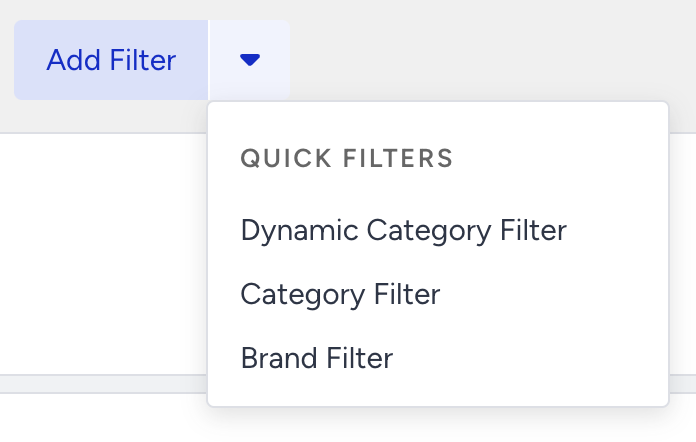
Quick filters for easy setup
Quick Filters are pre-configured filters tailored for different page types. To apply a Quick Filter:
Click the arrow next to the Add Filter button.
Select a relevant quick filter.
Adjust the filter settings as needed.
Filtering by Category
Category filters are among the most powerful tools for creating upsell and cross-sell scenarios. They provide strong context and allow you to tailor recommendations to your catalog’s structure. When you work with hierarchical categories, you can achieve different outcomes depending on how precisely you filter.
Let’s walk through an example using a hierarchical category tree.
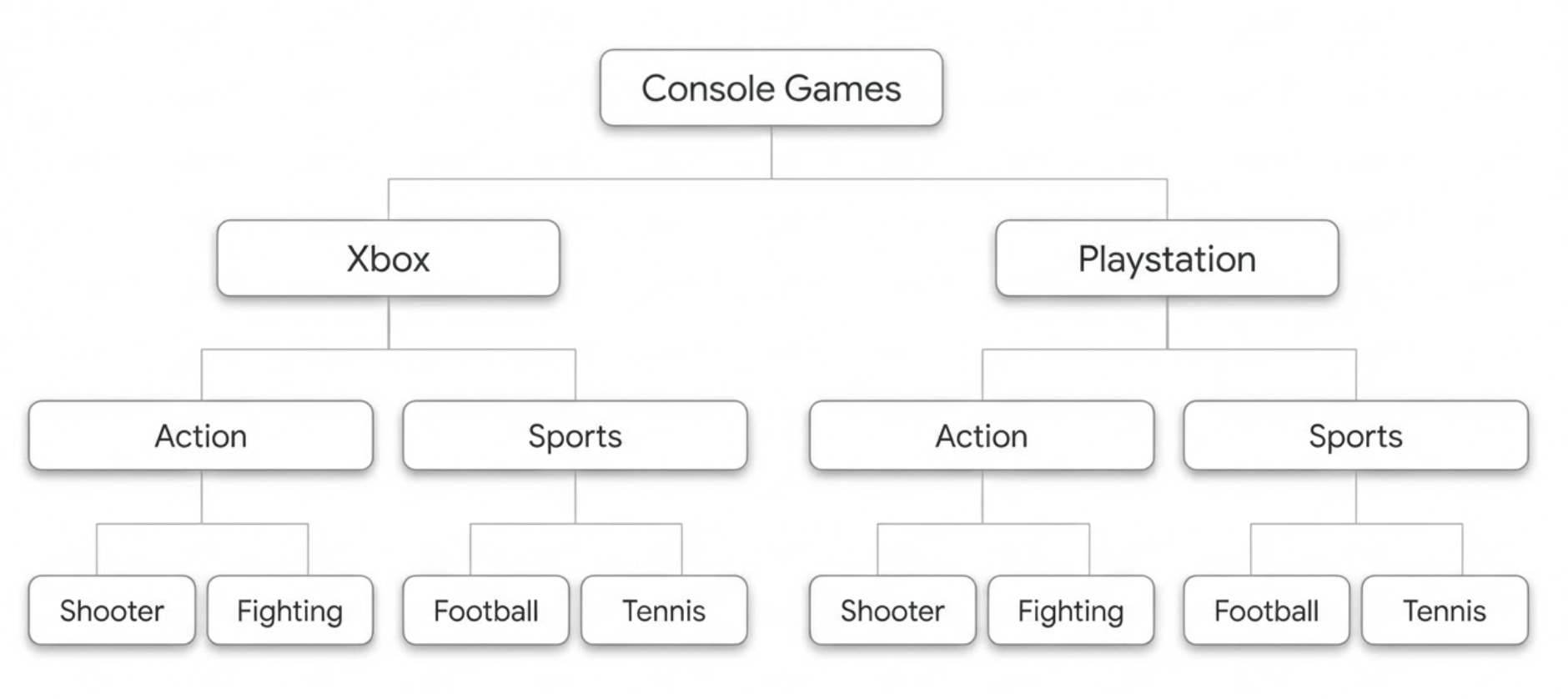
If you want to show Tennis games, and the platform does not matter, you can simply filter by the Tennis category.
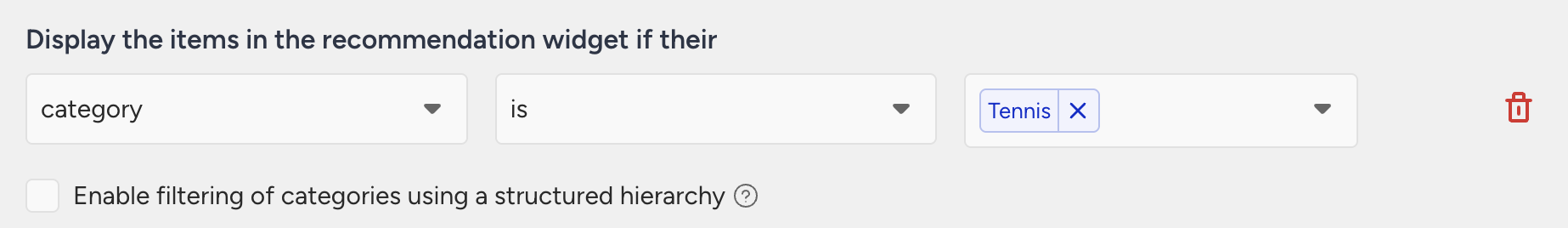
Recommendations can include any product that has Tennis in its category array. A product under [Console Games, Xbox, Sports, Tennis] or [Console Games, PlayStation, Sports, Tennis] can be recommended.
If you want Tennis games only for PlayStation, you can use the “Enable filtering of categories using a structure hierarchy” option. This lets you select a specific category path for precise filtering.

Recommendations will include only products that match the full path [Console Games, PlayStation, Sports, Tennis].
Let’s say you want to show products in the same categories as the visitor is currently viewing.
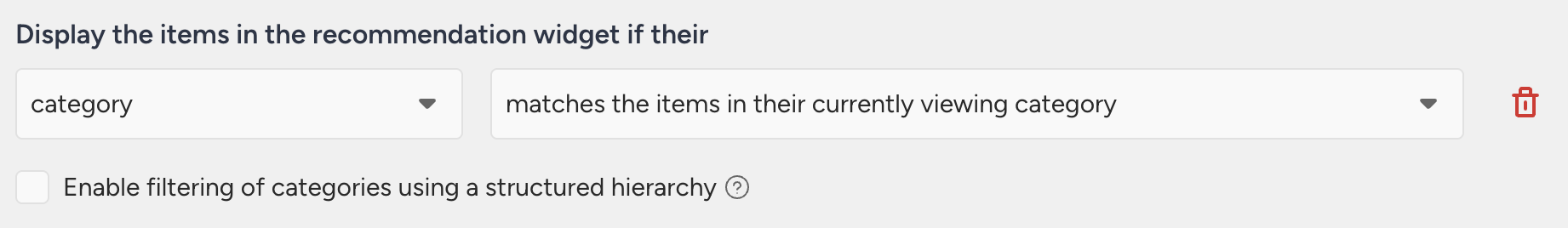
If a visitor is currently browsing Console Games > Xbox > Action, recommended items will be selected from products categorized under [Console Games, Xbox, Action]. Products that belong to a deeper category path, such as [Console Games, Xbox, Action, Shooter], may also be recommended, since the first three category levels match the visitor’s current path
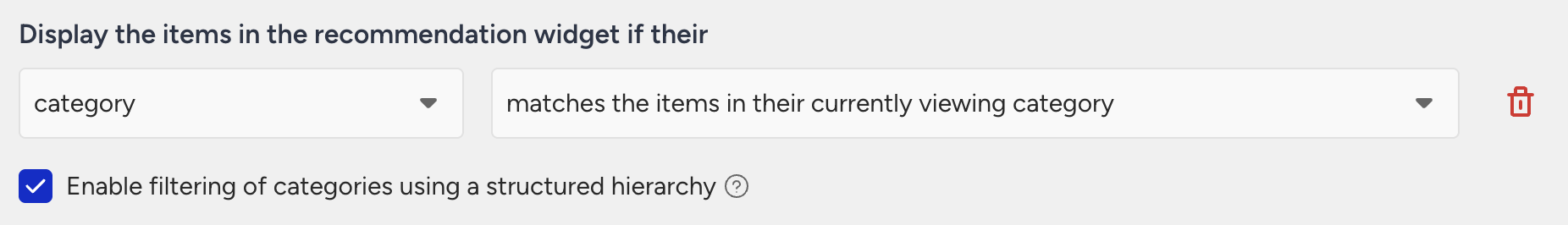
If a visitor is currently browsing Console Games > Xbox > Action, recommended items will only be selected from products that exactly match the category path [Console Games, Xbox, Action]. Products assigned to a deeper category path, such as [Console Games, Xbox, Action, Shooter], will not be recommended, as the path does not match exactly
Similarly, if a visitor is browsing Console Games > Xbox > Action > Shooter, recommended items will only come from products assigned to the exact category path [Console Games, Xbox, Action, Shooter]. Products categorized under [Console Games, Xbox, Action] will not be recommended, since they do not meet the exact path requirement.
If you want to show items from the user’s current category but want a fallback when there aren’t enough products, you can expand the scope to the parent category.
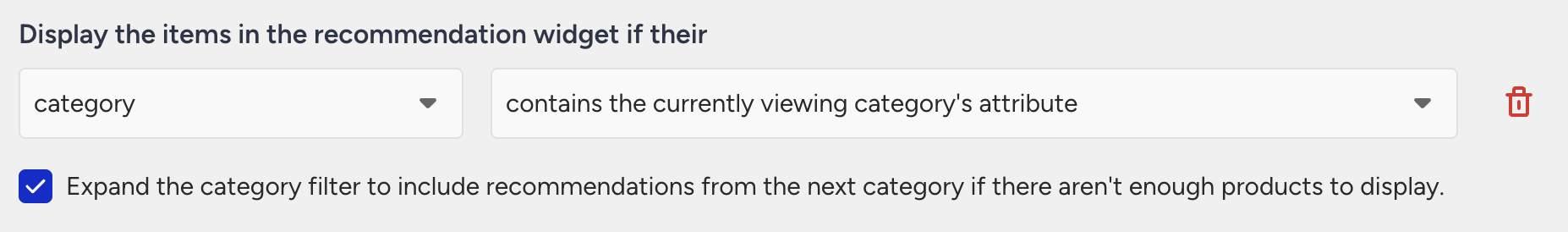
If a user is currently browsing Console Games > Xbox > Action > Shooter, recommended items will primarily be selected from products categorized under [Console Games, Xbox, Action, Shooter].
If there are not enough products to populate the recommendation slot, the system will broaden the selection to include products categorized under [Console Games, Xbox, Action]. In this case, recommendations may include products from multiple subcategories, such as both Fighting and Shooter.
Best practices for practical recommendations
Balance personalization with discovery: Exclude redundant products while ensuring users still see fresh recommendations.
Test different filter settings: Experiment with exclusion periods and attribute affinities to find what works best.
Monitor conversion rates: Analyze performance data to refine your recommendation strategy over time.
Use filters strategically: Here are some real-life examples of how filters can be applied to improve recommendation strategies:
Filtering use cases
Exclude discounted items:
Use category + is not + Discount to remove discounted products if you want to highlight premium offerings.
Show only high-value products:
Use price + is more than + $100 to focus on high-value items.
Highlight new products:
Use date added + is within + last 30 days to feature recently added products.
Exclude out-of-season products:
Use season + is not + Winter to avoid recommending winter items in summer.
Promote specific brands:
Use brand + is + Brand X to spotlight a preferred brand.
Show same branded products as the user is currently viewing:
Use brand + matches the item they're currently viewing to recommend products from the same brand as the product user is currently viewing to maintain consistency in recommendations.
Show same category products as the user is currently viewing:
Use category + is + matches the items in their currently viewing category to surface alternatives within the same category the user is viewing.
How does contains filter work?
The contains filter allows you to filter product attributes by matching part of a value. If the specified value is found within the attribute, the product will be included in the recommendation.
For example, suppose you have a set of products with group codes like ABC123, ABC124, ABC125, and so on. If you want to recommend products from this group but there are too many codes to select individually from the filtering dropdown, you can use the filter: group code + contains + ABC. This will return all products whose group code contains "ABC".
When used with an array of strings, the filter will check each item in the array. If any item contains the specified value, the product will be included in the results.