MindBehind offers built-in UCD functions that allow teams to interact with customer information directly through the chatbot, eliminating the need for additional backend services. These functions enable the retrieval of user attributes and the application of updates in a standardized manner, ensuring consistent and reliable communication with Insider One’s Unified Customer Database.
This guide explains how MindBehind uses UCD integration to access, update, and manage end-user profile data through chatbot interactions.
It covers the full setup process, the implementation flow, detailed explanations of each available UCD function, and practical usage patterns for applying these functions within a MindBehind chatbot.
Prerequisites
Before using UCD functions in MindBehind, make sure you complete the required setup steps outlined below to ensure secure access and proper configuration.
1. Generate an API Key from the InOne Panel
To use UCD functions within MindBehind, you must generate an API key from your own InOne panel in accordance with data security and access management requirements. After the API key is created, it should be shared following secure transmission practices: the encrypted key must be sent through one communication channel, and the password through a separate channel.
1.1. Navigate to InOne > your username > Settings > InOne Settings > Integration Settings.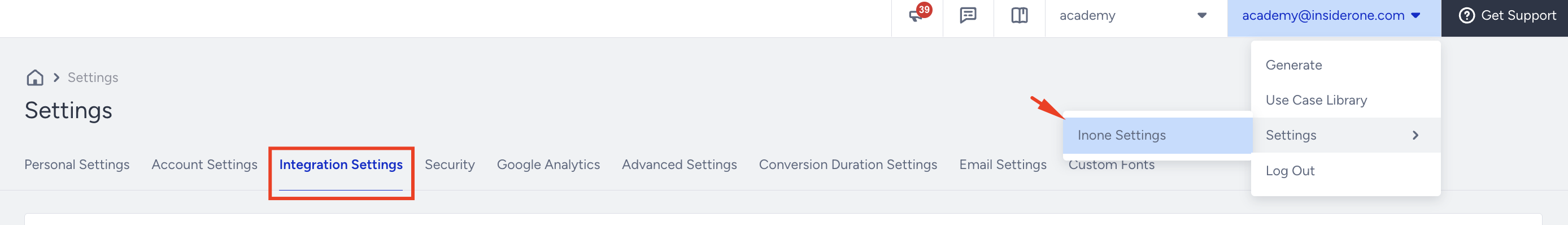
1.2 Scroll down and click the Generate API Key button. 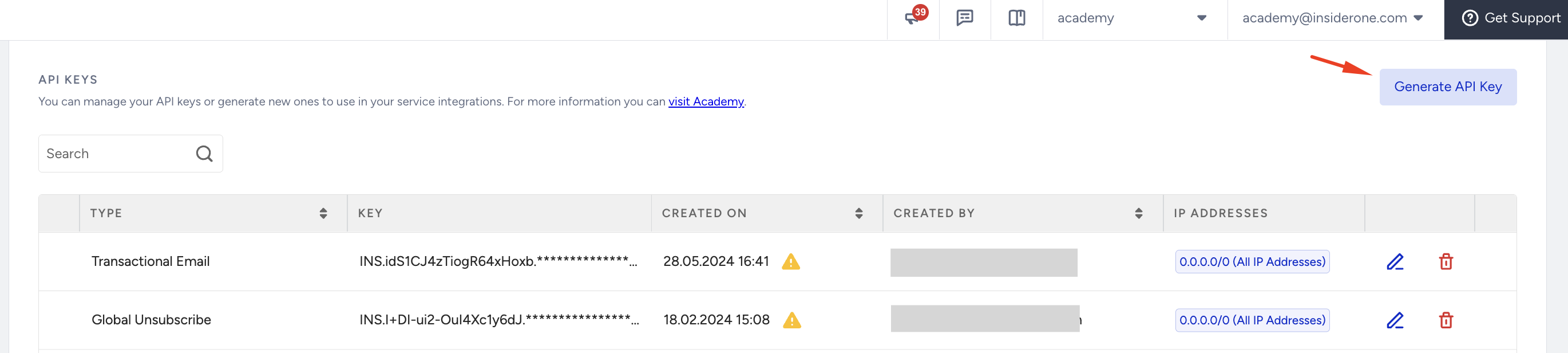
1.3. Select the Unified Customer Database from the list and click Continue.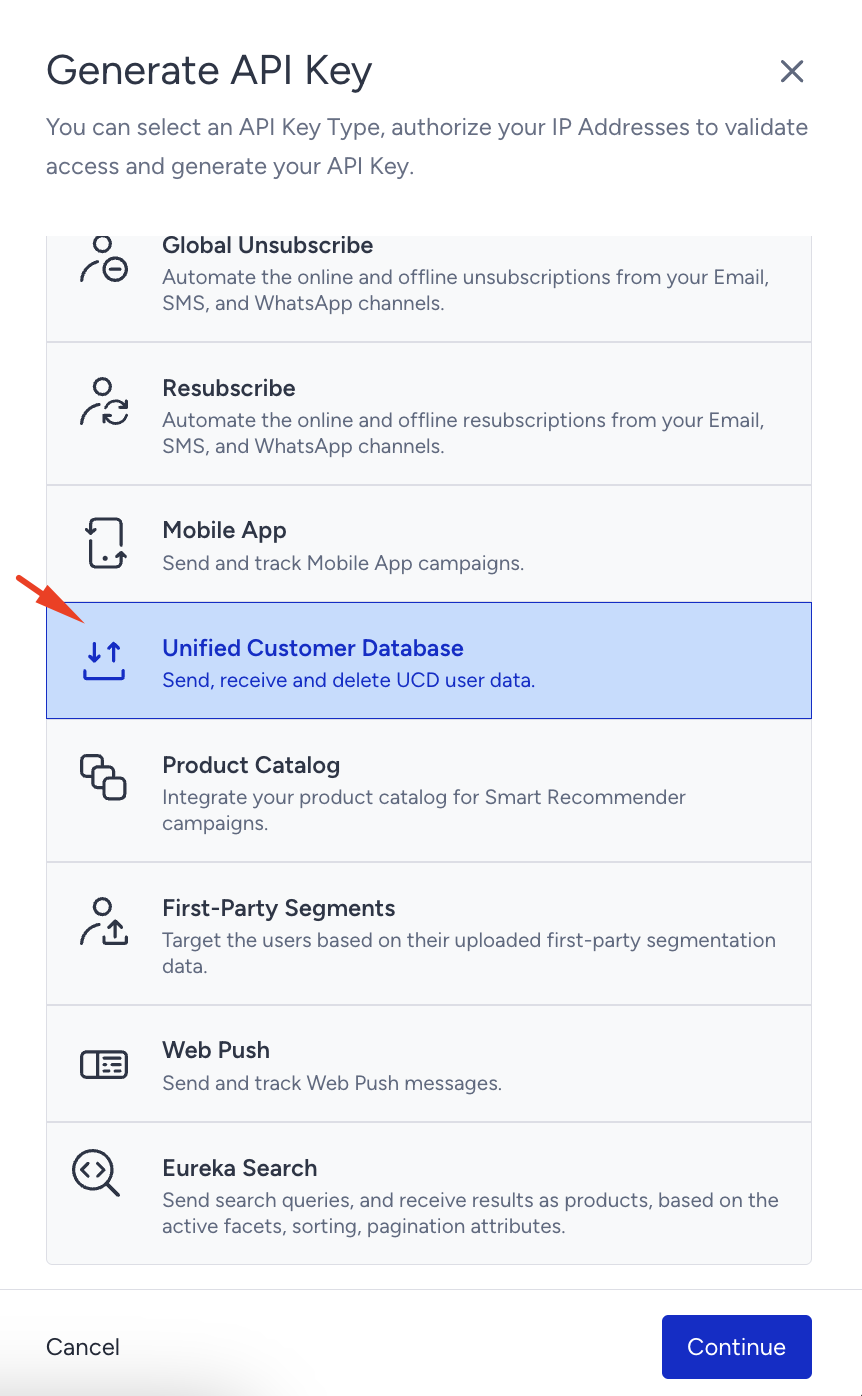
1.4. After you obtain the API key, you will use it in the following stages of the setup and integration process.
2. Configure the secret in MindBehind
This section provides the step-by-step guide for creating the Secret Manager configuration used by all UCD functions.
2.1. Go to the Code Station tab on MindBehind and click Secret Manager.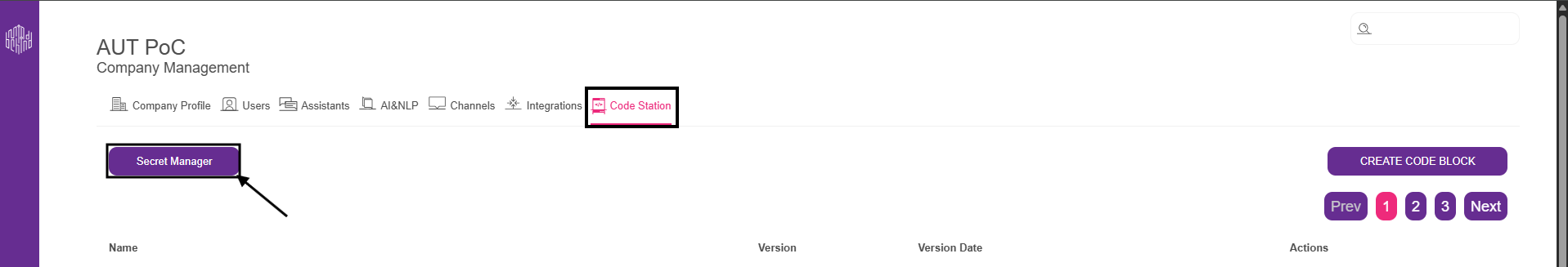
2.2. Click the Create Secret button.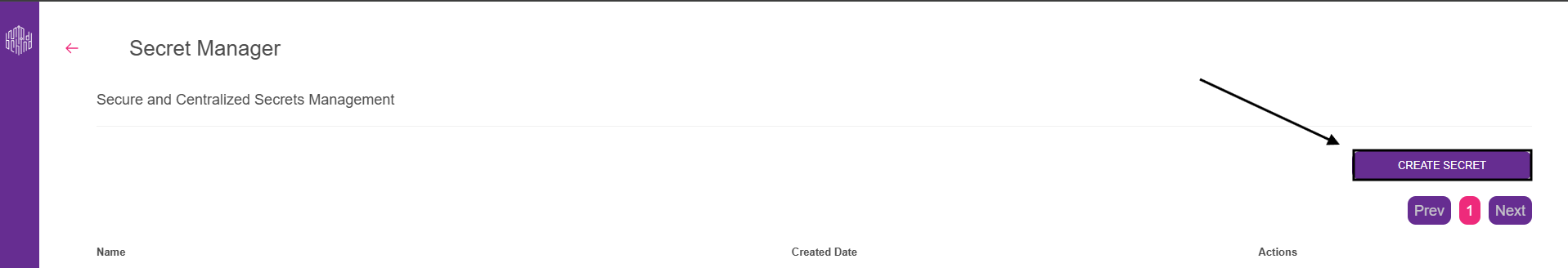
2.3. While creating the secret, enter the values listed in the table below into the corresponding fields shown on the screen. After filling them in, click the Add button for each entry, then select Create Secret.
Property Key | Property Value |
|---|---|
| API key obtained from the InOne panel |
| Partner InOne panel name |
| Fixed: |
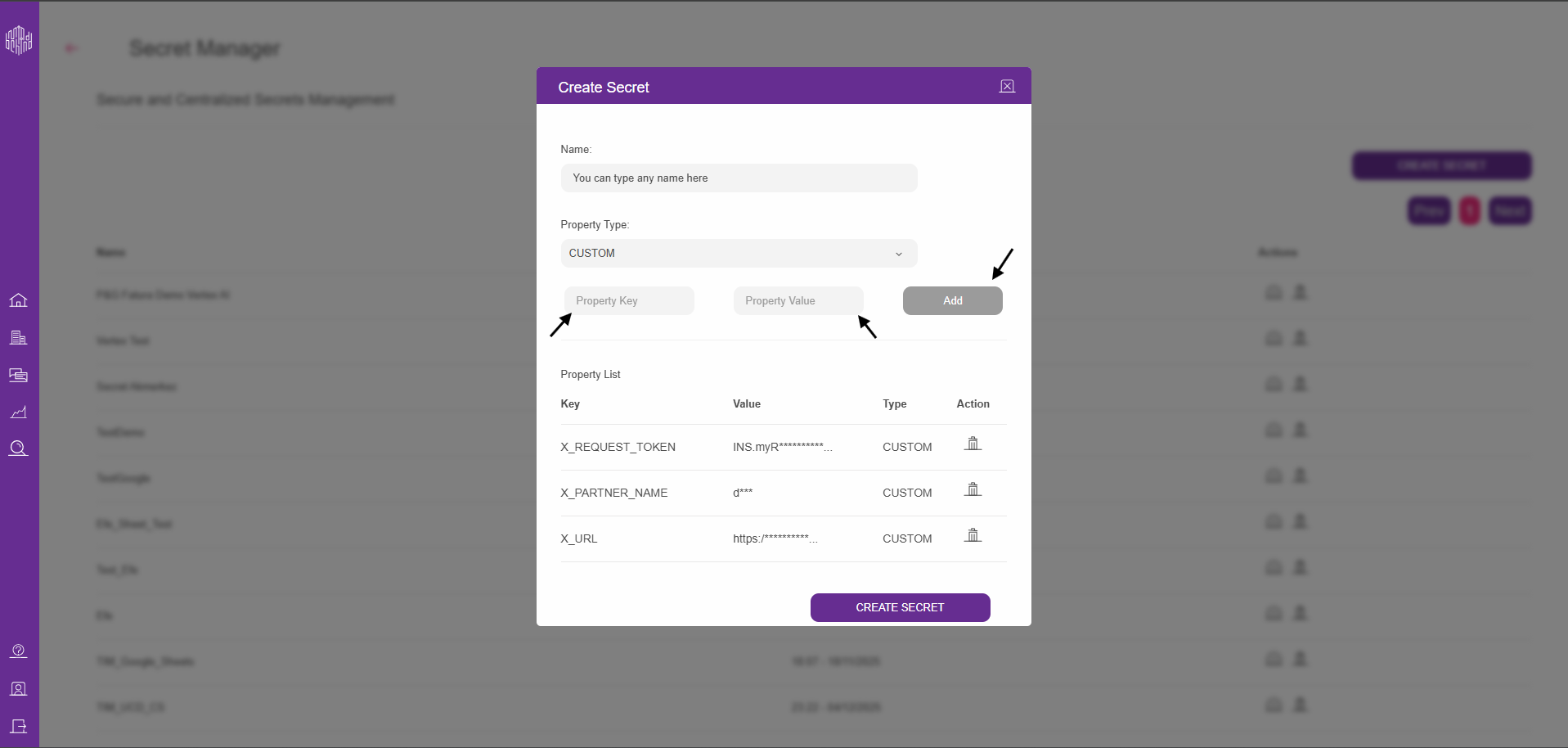
2.4. After creating a secret, click Create Code Block to create your code block.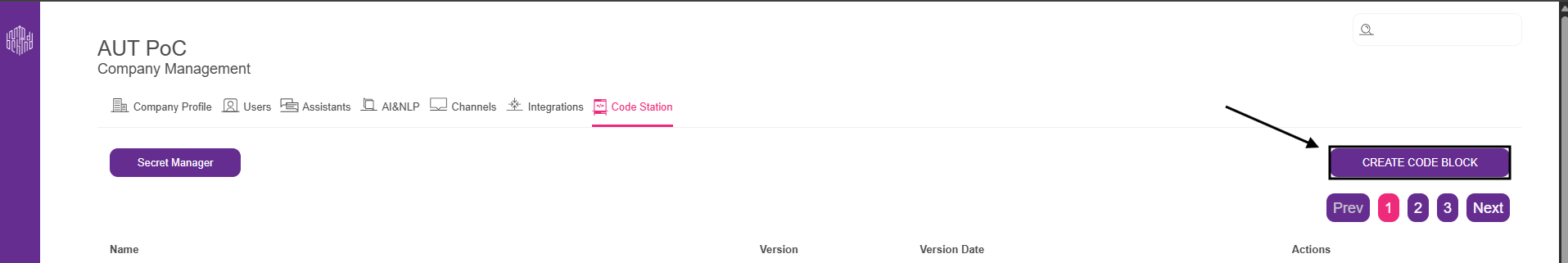
2.5. Select the Create From Template option.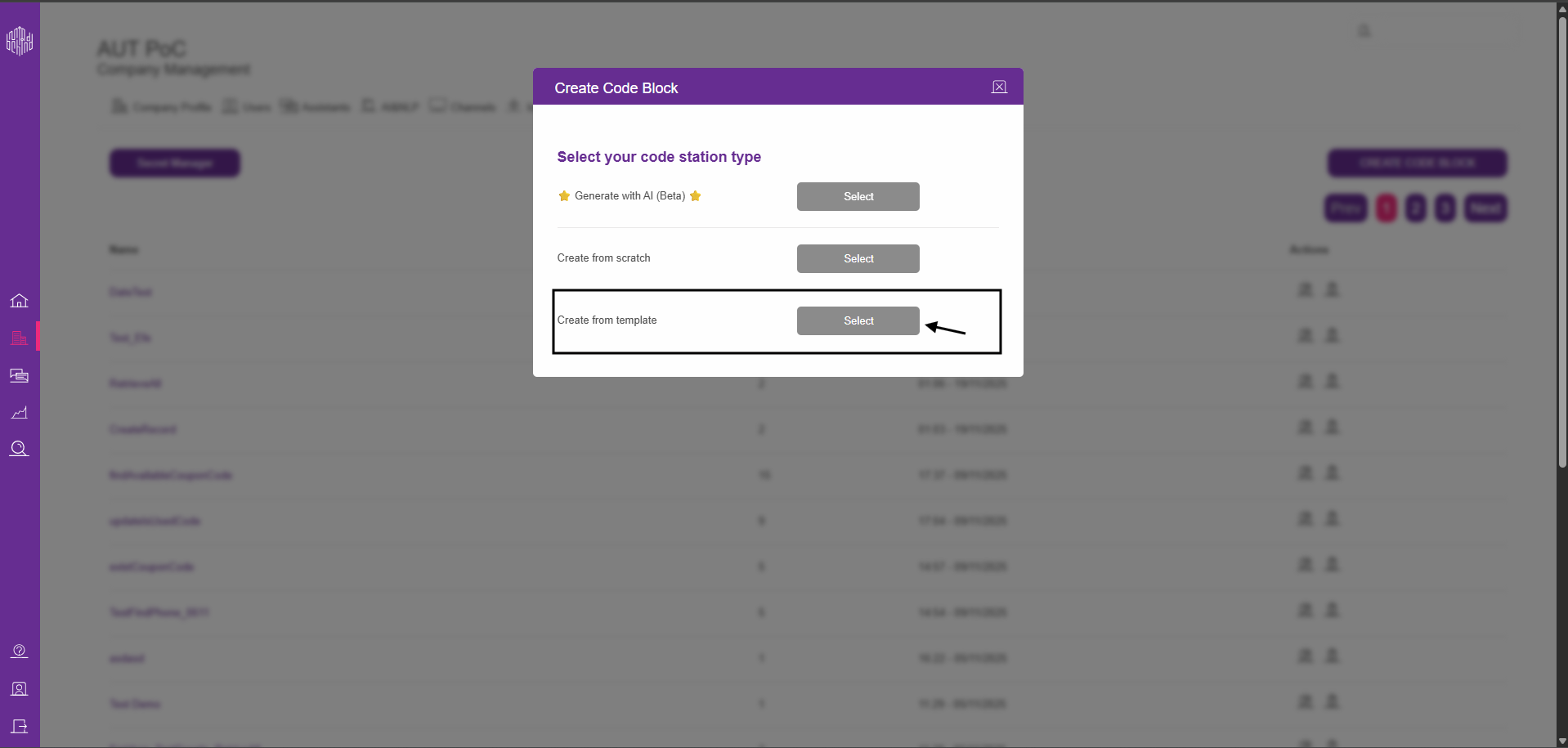
2.6. Select the Ucd-3 code block template.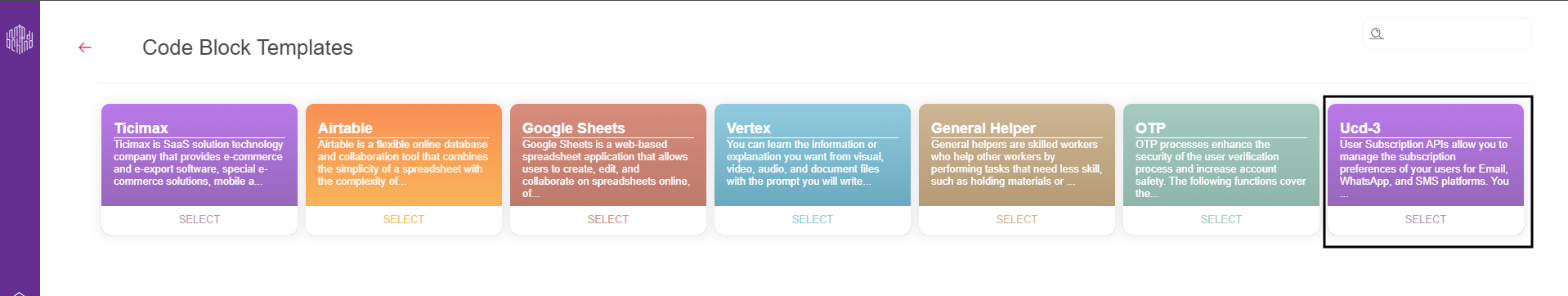
2.7. You can choose any template that suits your case from the dropdown. 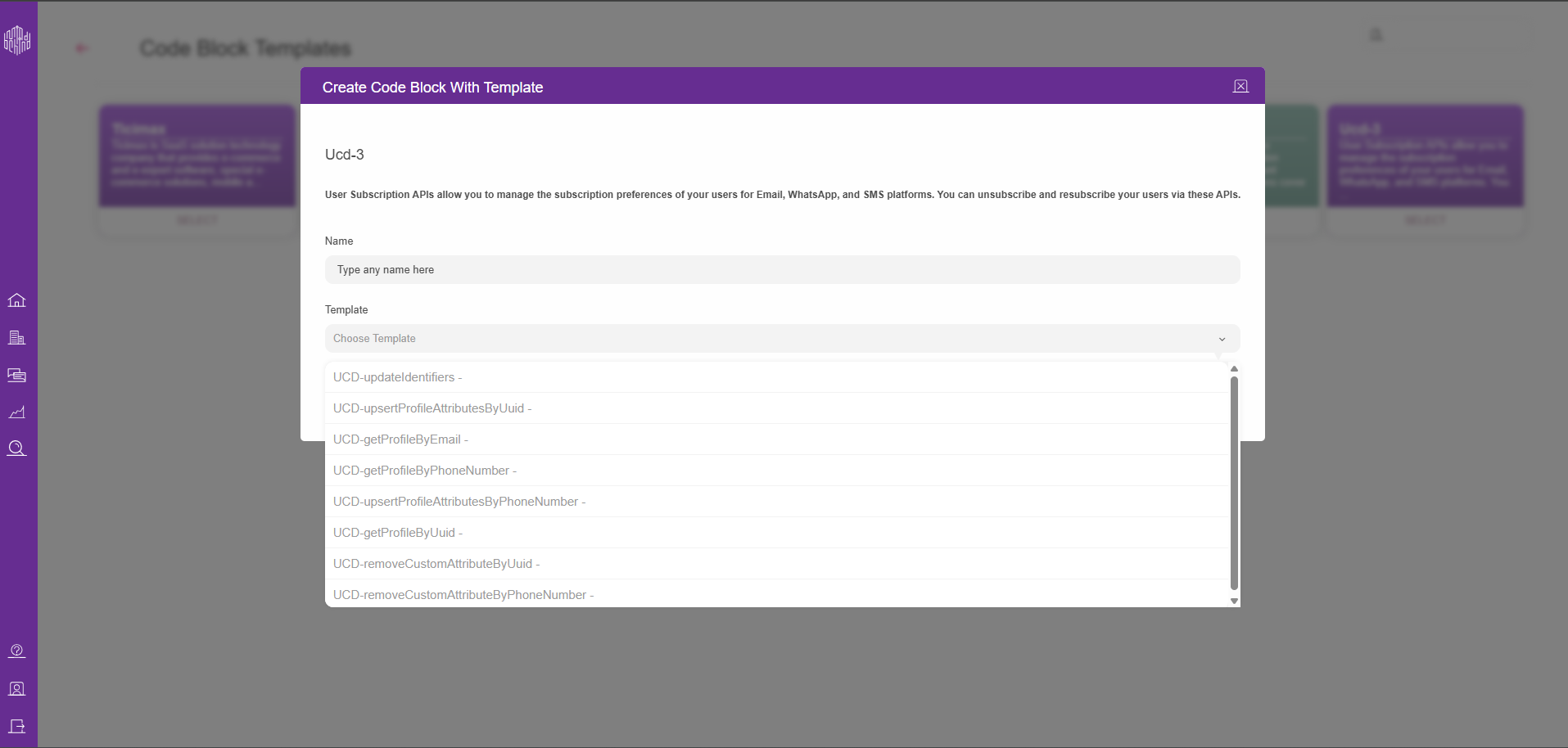
2.8. After selecting the template you want to use, click the Create Code Block button.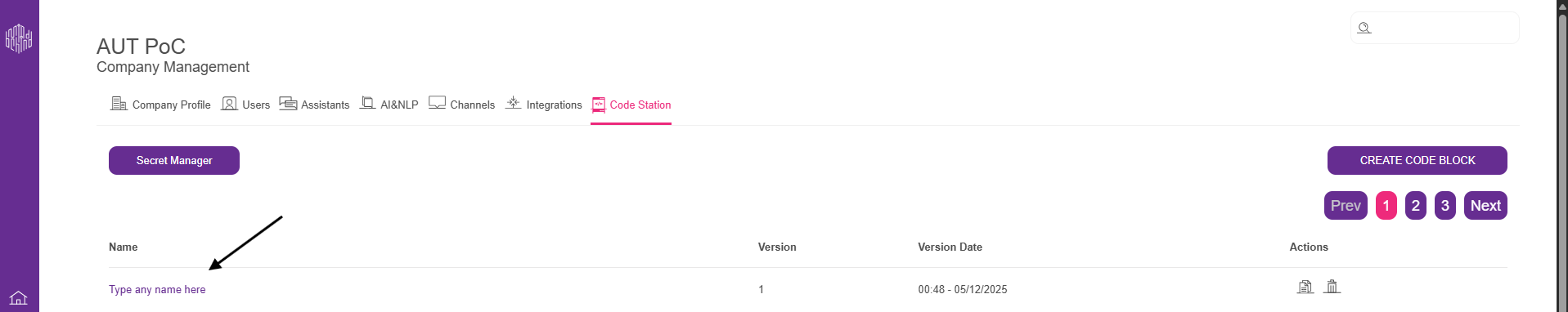
2.9. Select the secret you created earlier and click Save.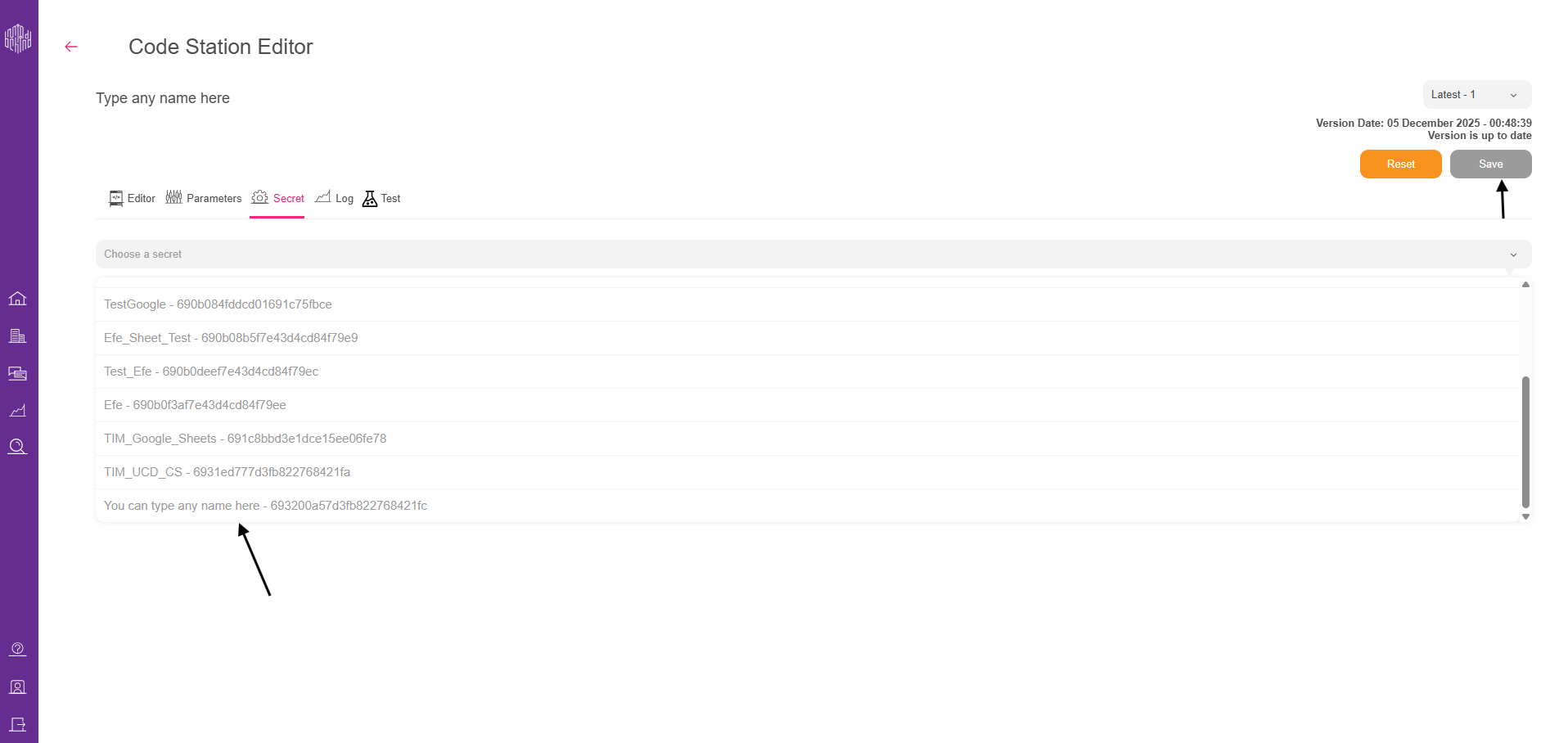
Available UCD functions and their usage
This section outlines the available UCD functions in MindBehind and explains how each function is used to retrieve, update, or manage end-user profile data within chatbot flows.
Retrieve user attribute information (Get Profile)
The functions below are used to fetch a user's profile attributes directly from the UCD via the chatbot.
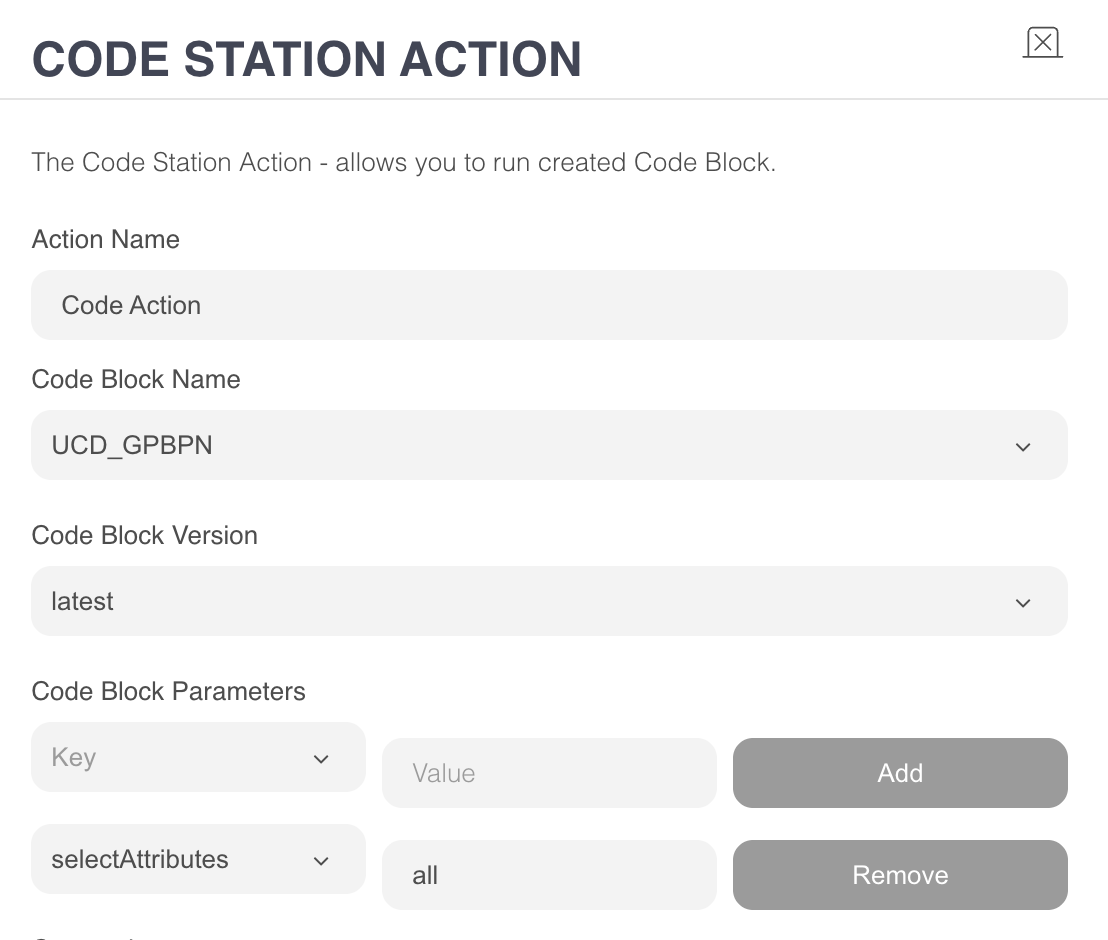
getProfileByPhoneNumber
Purpose: Retrieves the user’s profile attributes from UCD using their phone number. This function returns specific fields such as
city,whatsapp_optin, or any other selected attributes, depending on the request configuration.Parameters & Inputs:
phone (input): The phone number obtained from the bot. In WhatsApp bots, this value is captured automatically. If a phone input is provided, the function uses that value; if not, it defaults to the WhatsApp user’s phone number.
selectAttributes (CodeStation dropdown parameter): Specifies which attributes should be returned. This can be "all" or a comma-separated list such as
whatsapp_optin,city(no spaces).
Example Response:
{
"isUserFound": "true",
"whatsapp_optin": true
}
getProfileByUuid
Purpose: Retrieves the user’s profile attributes from UCD using their UUID. This function operates the same way as getProfileByPhoneNumber, except that it requires a UUID instead of a phone number.
getProfileByEmail
Purpose: Fetches the user’s profile attributes from UCD using their email address. The parameter structure and overall behavior are identical to those of getProfileByPhoneNumber, except that this function accepts an email input.
Remove custom attributes
These functions are used to delete custom attributes defined within a user’s profile in the UCD.
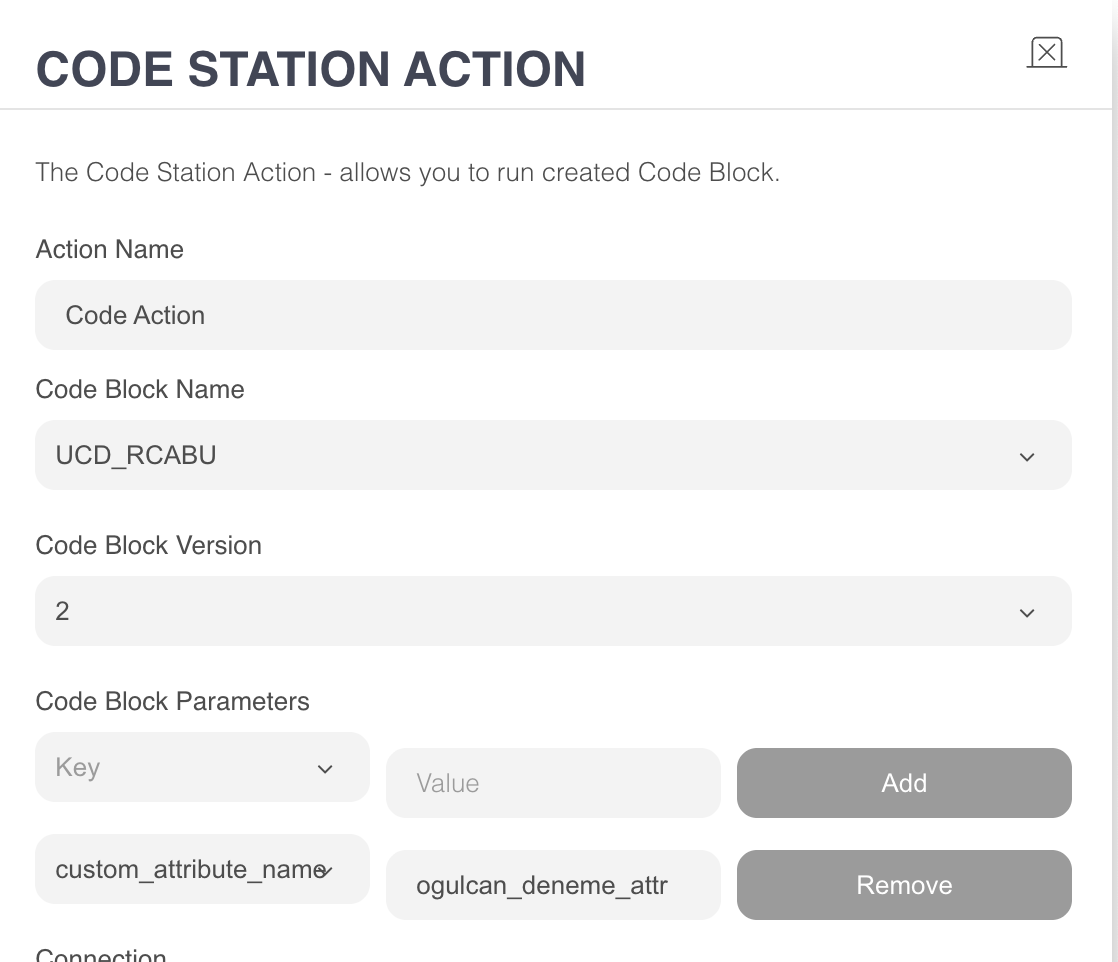
removeCustomAttributeByPhoneNumber
Purpose: Deletes a specific custom attribute from the user’s UCD profile using their phone number.
Parameters & Inputs:
phone (input): The phone number was retrieved from the bot. In WhatsApp bots, this value is captured automatically.
If a phone input is provided, it will be used; otherwise, the function defaults to the WhatsApp user’s phone number.custom_attribute_name (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The name of the custom attribute to be removed.
Custom attribute names must be provided without the
c_prefix. For example, uselast_visited_category_nameinstead ofc_last_visited_category_name.
Example Response:
{
"isRemovedAttributes": true
}
removeCustomAttributeByUuid
Purpose: Removes a specific custom attribute from the user’s UCD profile using their UUID. The parameters and behavior are identical to removeCustomAttributeByPhoneNumber, except that this function requires a UUID input instead of a phone number.
Update or add profile attributes
These functions are used to add new attributes or update existing attribute values within a user’s UCD profile.
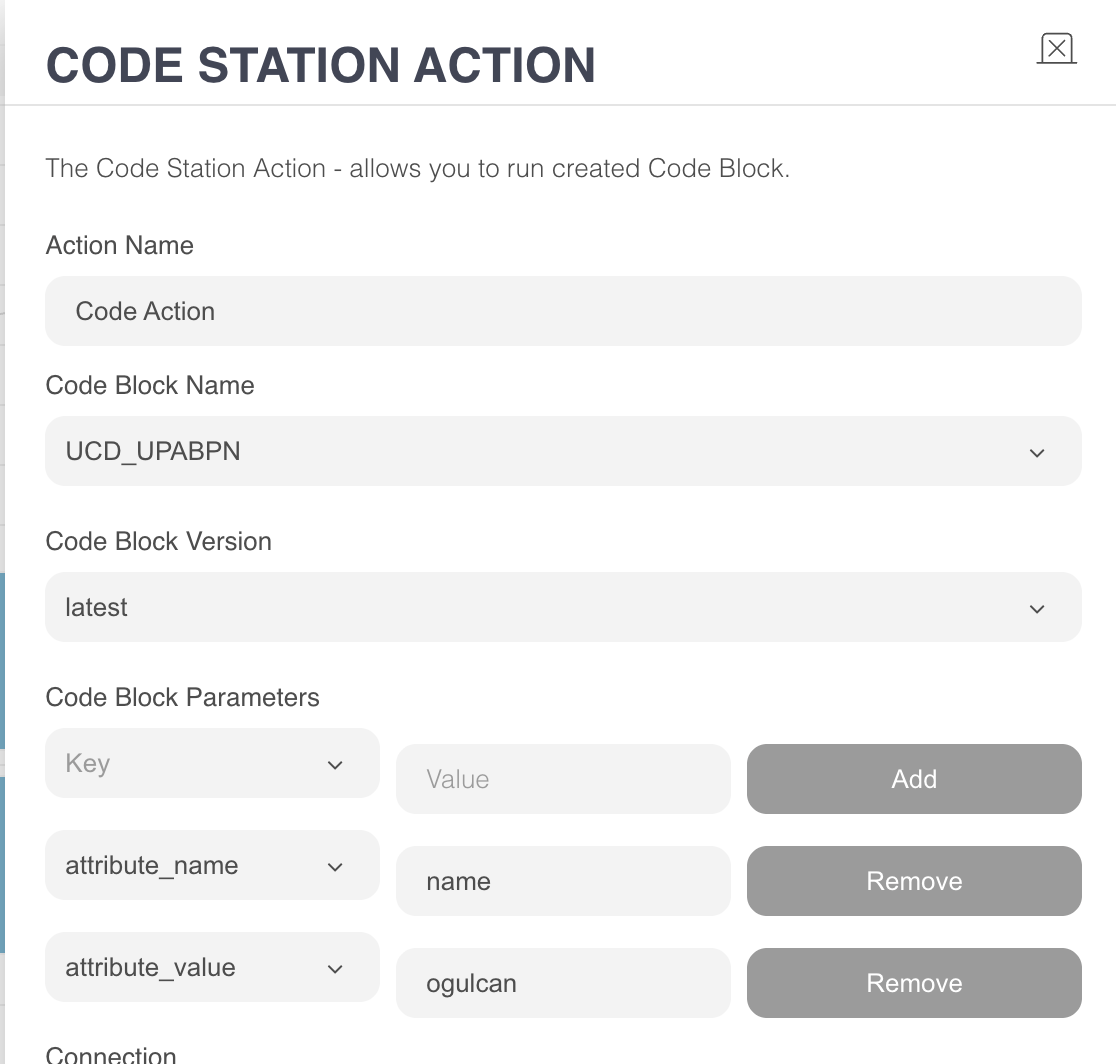
upsertProfileAttributesByPhoneNumber
Purpose: Updates or adds a profile attribute in the user’s UCD profile using their phone number. Note that this function supports only string or boolean attributes—custom attributes are not supported.
Parameters & Inputs:
phone (input):
The phone number obtained from the bot. In WhatsApp bots, this value is captured automatically.
If a phone input is provided, it is used; otherwise, the function defaults to the WhatsApp user’s phone number.attribute_name (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The name of the attribute to be updated.
attribute_value (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The new value to be added or updated.
Example Response:
{
"isUpdatedAttributes": true
}
upsertProfileAttributesByUuid
Purpose: Updates or adds a profile attribute in the user’s UCD profile using their UUID. This function behaves the same as upsertProfileAttributesByPhoneNumber, except that it requires a UUID input rather than a phone number.
Update identifiers
These functions are used to modify an existing identifier in the user's UCD profile, such as updating a phone number or replacing another key-value pair.
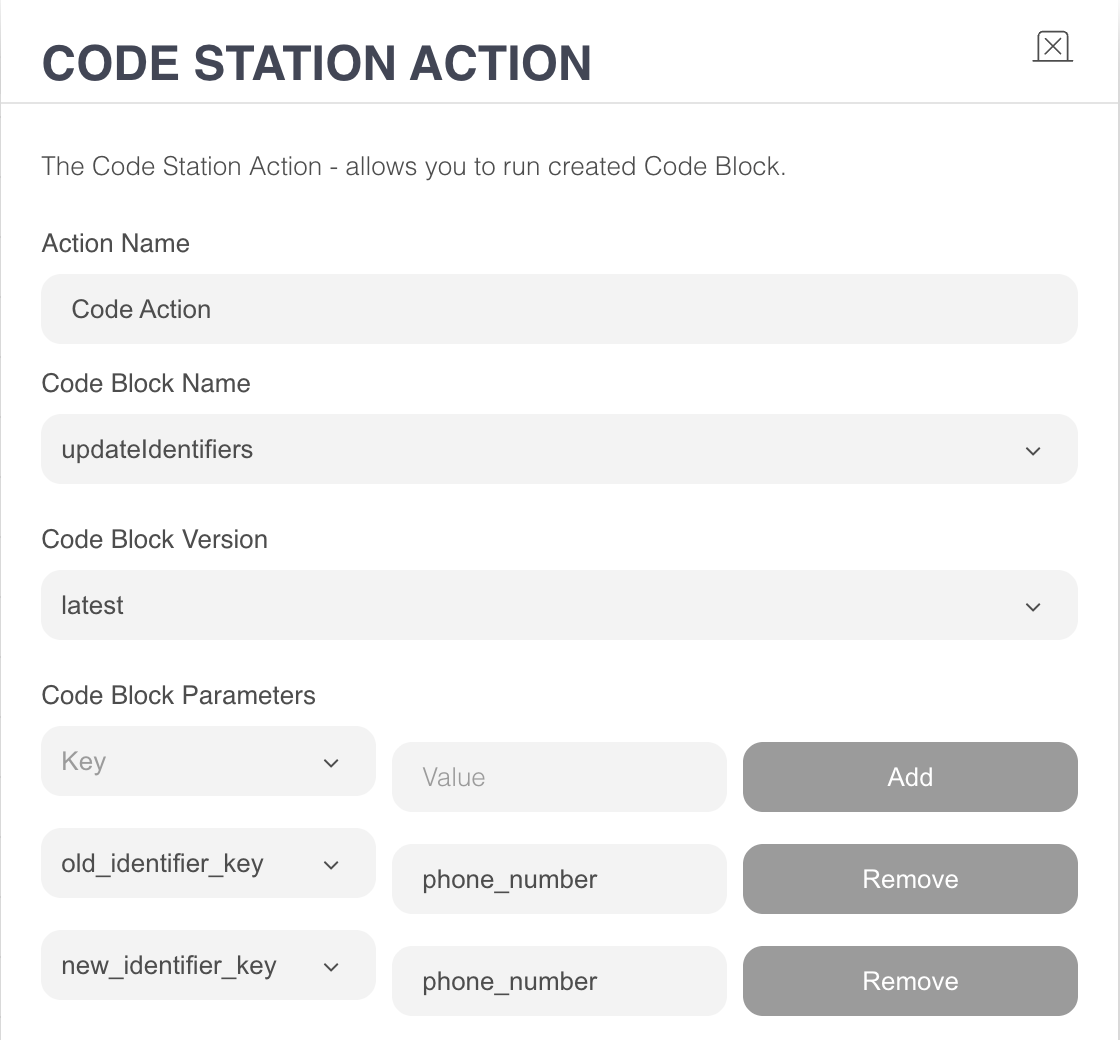
updateIdentifiers
Purpose: Replaces an existing identifier in the user’s UCD profile (e.g., phone number) with a new value.
Parameters & Inputs:
old_identifier_key (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The field to be updated (e.g., "phone_number").
old_identifier_value (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The current value of the identifier (e.g., +905414344817).
new_identifier_key (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The identifier field that will be set with the new value (typically the same key, e.g., "phone_number").
new_identifier_value (CodeStation dropdown parameter): The new value that will replace the old one (e.g., +905051234567).
Example Response:
{ "isUpdatedIdentifiers": true }
Implement UCD functions in MindBehind maps
In this section, you will find practical examples demonstrating how to use the templates described above within a chatbot flow. Each example illustrates where and how these functions are applied, providing a clear view of their real-world usage in MindBehind maps.
Retrieve a user profile (Phone, UUID, or Email)
UCD offers three profile-retrieval functions:
getProfileByPhoneNumber
getProfileByUuid
getProfileByEmail
Although each of them uses a different identifier, their overall behavior is identical.
The chatbot asks the user for the required identifier (phone number, UUID, or email).
The template is executed with selectAttributes set to "all" or a specific list of attributes.
UCD returns the user’s profile as key-value pairs.
The bot displays the retrieved data or uses it for decision-making.
A customer wants to check whether their contact preferences are updated.
Conversation sample:
User: “Show me my profile.”
Bot: “Please provide your phone number.”
→ UCD template retrieves the profile.
Bot: “Your current opt-in status is true, and your city is Istanbul.”
This scenario enables bots to personalize experiences or verify user identity using existing UCD records.
Remove a custom attribute
UCD provides two deletion functions:
removeCustomAttributeByPhoneNumber
removeCustomAttributeByUuid
These functions are used to remove custom attributes (e.g., last viewed category, abandoned cart flag, segmentation attributes).
Custom attribute names must be provided without the c_ prefix (as explained in the PDF).
The chatbot asks the user for the identifier (phone/UUID).
The template is executed with the custom attribute name to be deleted.
The bot confirms the deletion.
A user wants to reset or clear stored personalization data.
Conversation sample:
User: “Clear my browsing history.”
Bot: “Done! Your stored category preferences have been removed.”
This is often used in GDPR-related flows, preference resets, or when cleaner behavioral data is required for the next session.
Update or add standard profile attributes (Upsert)
To update (or create) standard profile attributes, UCD provides:
upsertProfileAttributesByPhoneNumber
upsertProfileAttributesByUuid
These functions support string and boolean values. They do not modify custom attributes.
Ask the user for the identifier (phone/UUID).
Collect the new attribute value (e.g., new email, preferred name, opted-in flag).
Execute the UCD template with the attribute name and value.
Confirm the update.
A user updates their name or contact information.
Conversation sample:
User: “I want to update my name.”
Bot: “Sure, what should your name be?”
→ Template runs
Bot: “Your name has been updated successfully.”
This is widely used in onboarding flows, profile-management screens, and cases where user data must stay synchronized between systems.
Update identifiers (Phone Number, Email, etc.)
The updateIdentifiers template is used when a core identifier needs to be replaced—for example, when a user changes their phone number or email address.
Ask the user for the existing identifier value.
Ask for the new value that should replace it.
Execute the template with:
old_identifier_key
old_identifier_value
new_identifier_key
new_identifier_value
Notify the user that the update was completed.
A customer switches to a new phone number and wants future communication routed there.
Conversation sample:
User: “I changed my phone number.”
Bot: “Please enter your current number.”
Bot: “Now enter your new number.”
→ Identifier updated
Bot: “Your phone number has been updated successfully.”
This function is especially useful for ensuring ongoing communication continuity across WhatsApp, SMS, and email channels.
Personalize the conversation using UCD outputs
Regardless of which UCD function is used, the returned values can be embedded into the chatbot messages or used for routing logic within the map.
Retrieve user profile via UCD.
Check the returned attributes (e.g., gender, city, opt-in, membership_tier).
Adjust the conversation path based on these attributes.
Conditional example:
If membership_tier = "gold" → show premium support menu
If city = "Istanbul" → display region-specific services
If whatsapp_optin = false → start opt-in collection flow
This creates a tailored customer journey without additional backend logic.