Recommendation algorithms are the core engine behind personalized experiences. Their performance depends on the quality of your data, the accuracy of their configuration, and the strength of the signals they receive from user behavior. This page helps you understand how algorithms work, monitor their health, and fine-tune their settings for the best results.
You will learn how to verify data prerequisites, review accuracy indicators, adjust look-back periods, and choose the right data sources.
Algorithm Accuracy
Each algorithm has its own calculation method, refresh interval, prerequisites, and configuration options. To ensure your strategies perform optimally, it’s important to verify that each algorithm is functioning correctly and receiving the necessary data to generate recommendations.
Navigate to Components > Recommendation Algorithms and Settings to check the status of your algorithms. Here’s how to ensure everything is in order:
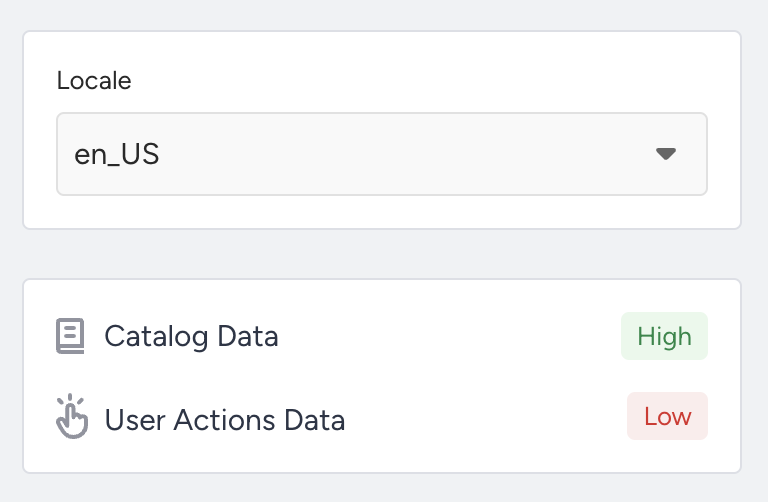
Locale Selection: Most algorithms operate based on user actions and catalog data segmented by locale. First, select the appropriate locale to view your data's health.
Data Status Indicators: After selecting a locale, you’ll see indicators showing whether catalog and user action data are available. This is essential for algorithms to generate accurate recommendations.
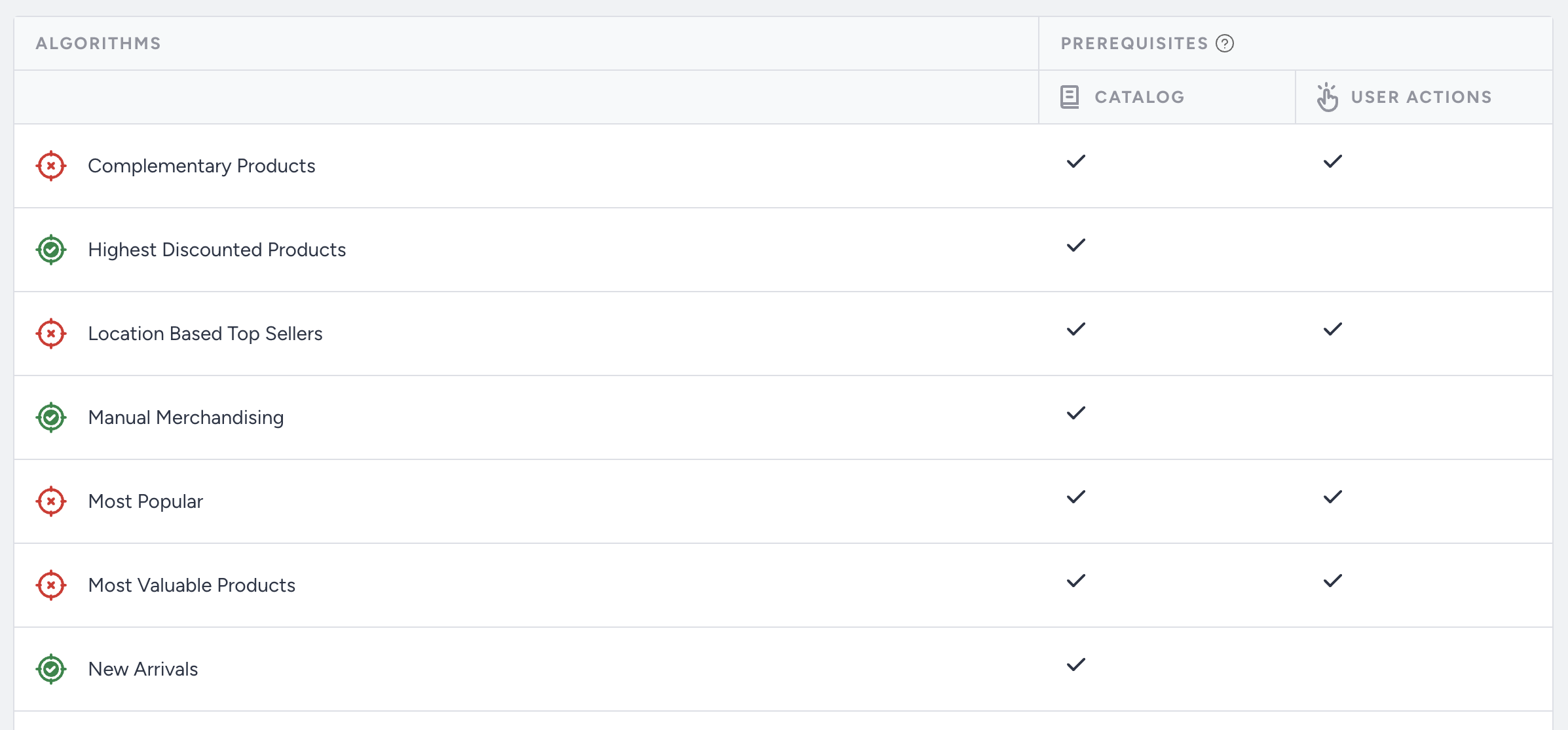
Prerequisite Check: Each algorithm has specific data prerequisites.
A green icon next to an algorithm means its prerequisites are met.
A red icon indicates missing or insufficient data, so the algorithm cannot function as expected.
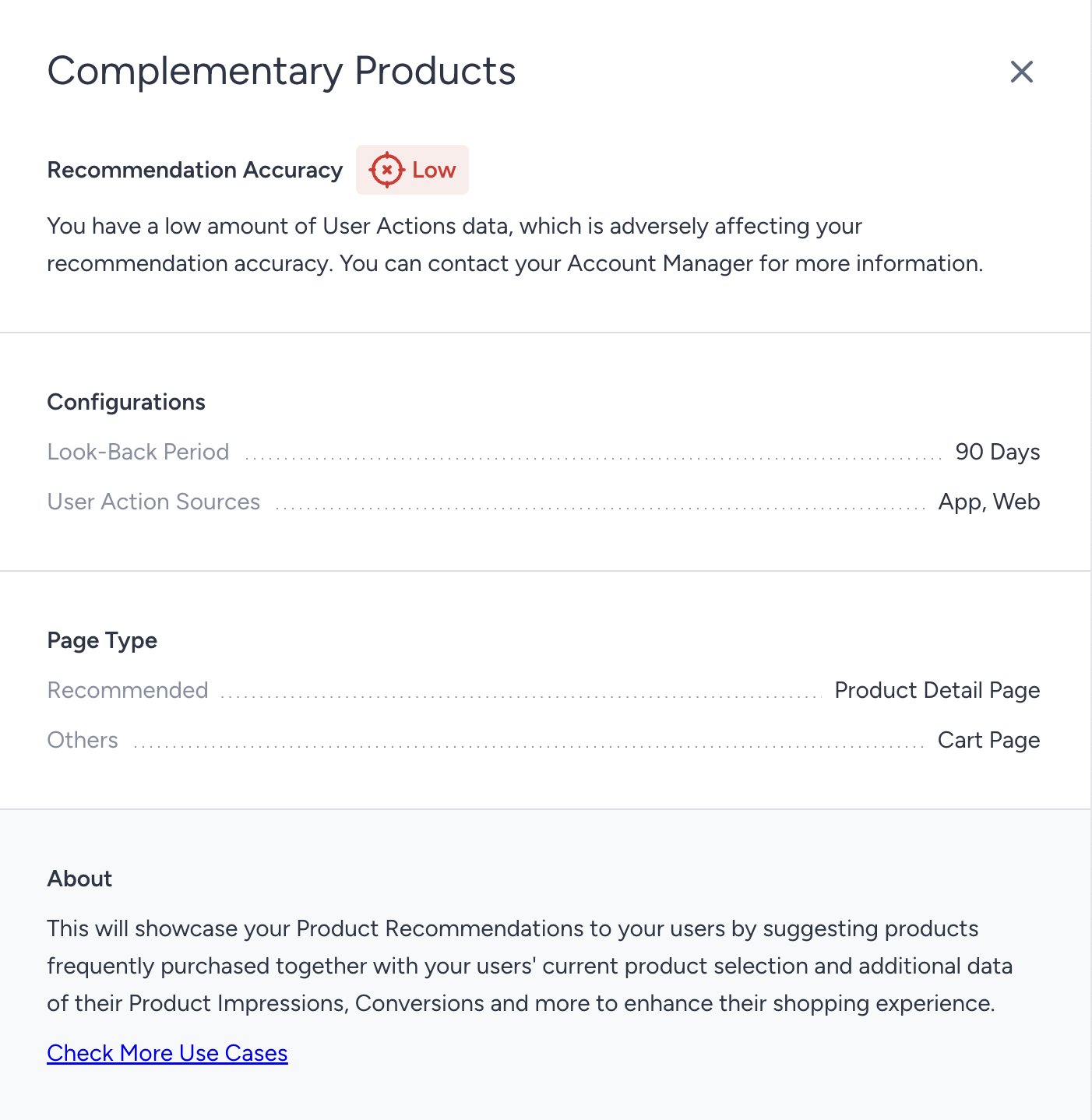
Diagnosing Low Accuracy: If an algorithm displays low accuracy, click on its name to open the Details Modal. This will provide insights into the cause, such as insufficient user actions or catalog coverage, helping you quickly troubleshoot and resolve data issues.
Algorithm Configuration
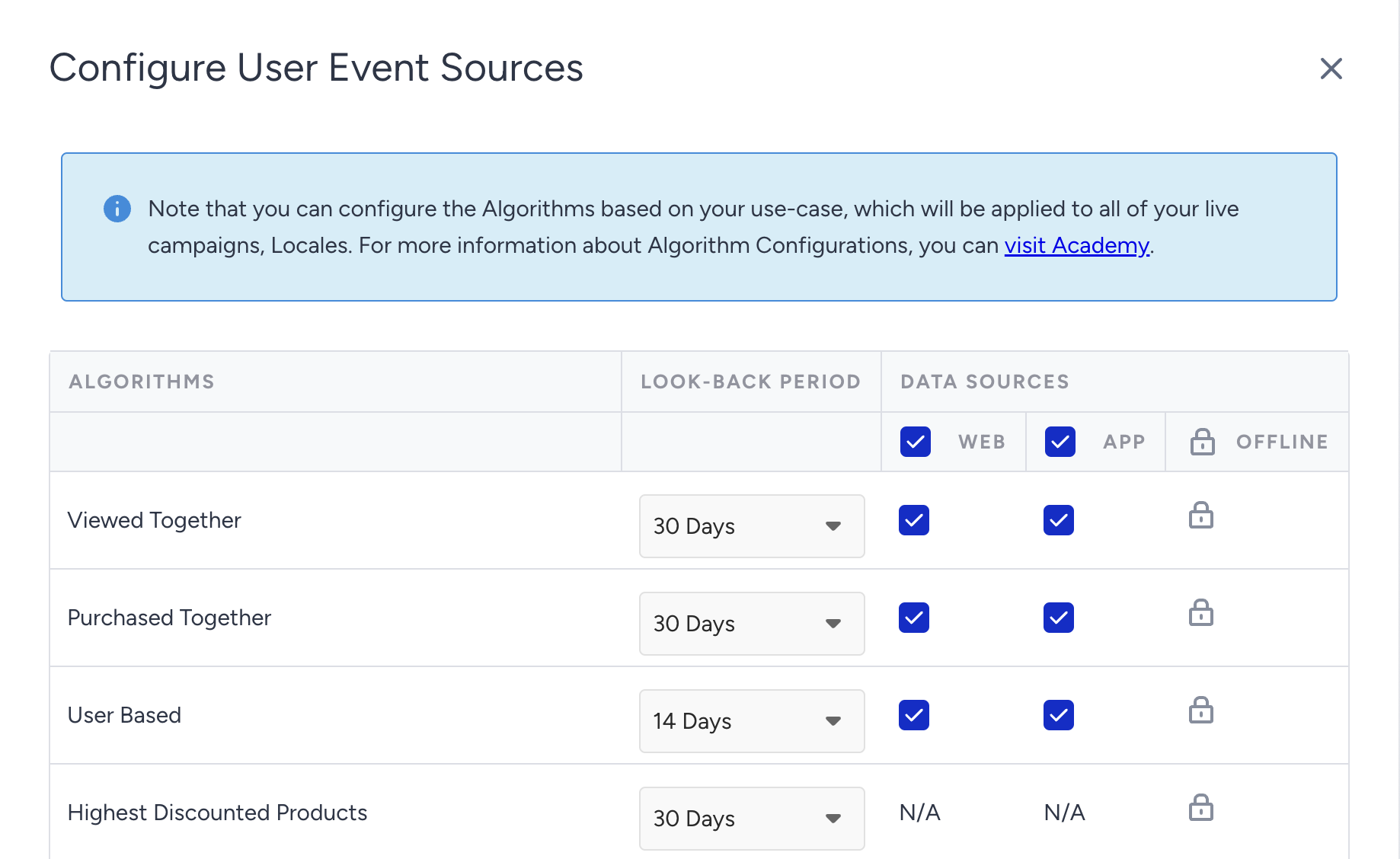
You can fine-tune algorithm behavior by adjusting look-back periods and data sources to better align with your business goals and user behavior.
Look-Back Period
The look-back period defines how many days of user event data the algorithm should consider. Choosing the right time window keeps recommendations fresh, relevant, and responsive to changes in demand.
Use shorter windows (e.g., 7 days) to highlight recent trends, such as a “Hot This Week” widget.
Use longer periods (14–30 days) to maintain stability in low-traffic periods or when product trends shift slowly.
Each algorithm may require different historical data, so experiment and monitor performance.
Data Sources
Customers engage across multiple touchpoints: web, mobile apps, and offline (e.g., in-store). Each channel generates valuable behavioral data that can improve recommendation accuracy.
You can enable the relevant data sources, Web, App, and Offline, per algorithm, to ensure your strategy reflects the full customer journey.
How to use offline events
Offline user events can be sent through the Upsert API.
To use these events as offline source in your recommendation algorithms the locale parameter in the event object is required. Without this parameter, the events will not be processed as offline data for recommendations.
To configure these settings:
Navigate to the Recommendation Algorithms.
Click the Configure button at the top right.
Adjust the Look-Back Period and Data Source settings for each algorithm to match your use case.
Recommendation Settings
To reach the Recommendation Settings, navigate to Components > Recommendation Algorithms. Switch to the Recommendation Setting tab.
Product Variant Exclusion
Products in your catalog may have multiple variants based on attributes such as size, color, or style. For example, a sneaker may be available in different colors or sizes, and each of these options is considered a variant. This setting allows you to choose whether variants of the same product should be shown or excluded.
If you choose to exclude variants, only the highest-performing variant within each product group will be displayed, while all other variants from the same group will be removed.

Dynamic Value Configuration
Operators such as “matches the item they’re currently viewing” do not require a manual value selection. These operators work dynamically by filtering recommendations based on the product a user is currently viewing. As a result, recommendations automatically adapt to the user’s browsing context and remain relevant.
Two ways are available for Insider One to retrieve an attribute’s value from the product a user is viewing in order to apply dynamic filtering:
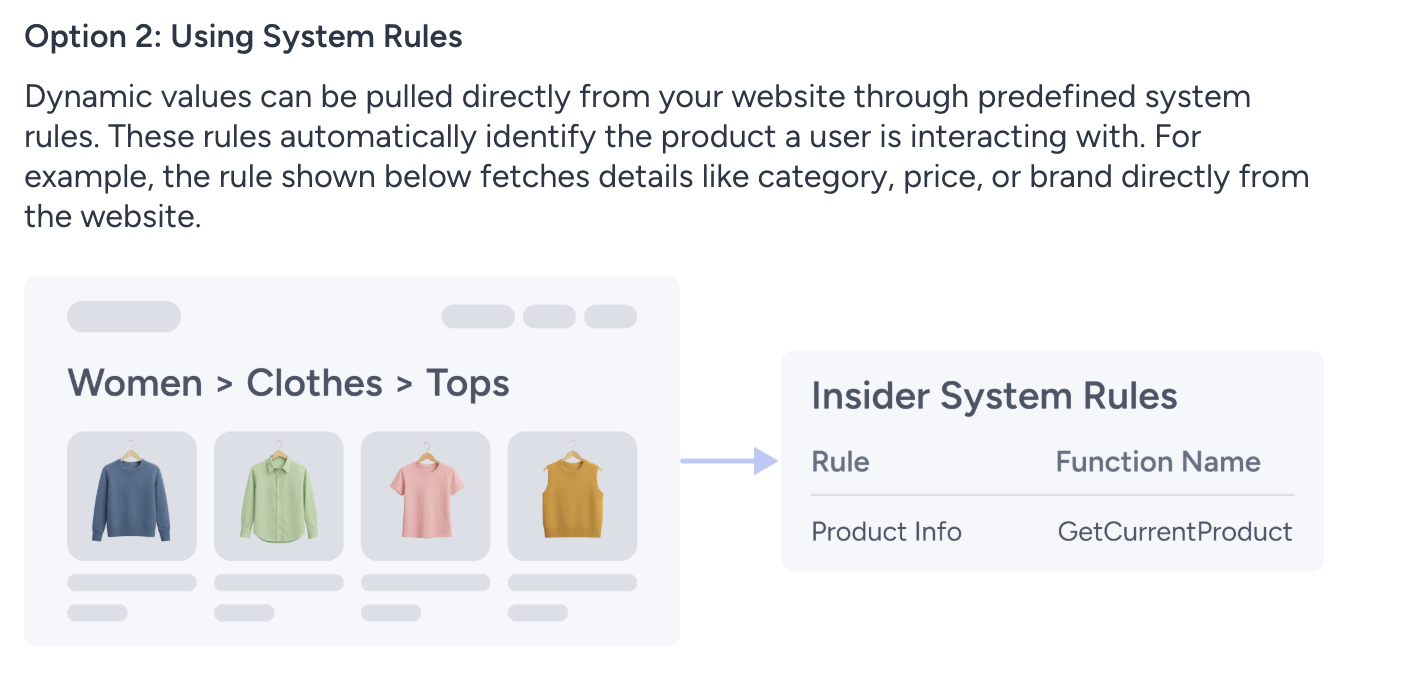
System Rules
Dynamic values are retrieved directly from your website using system rules.
If the campaign is displayed on a product page, the getCurrentProduct() system rule is used to retrieve the attribute value.
If the campaign is displayed on a category page, the getCategories() system rule is used to retrieve the category value.
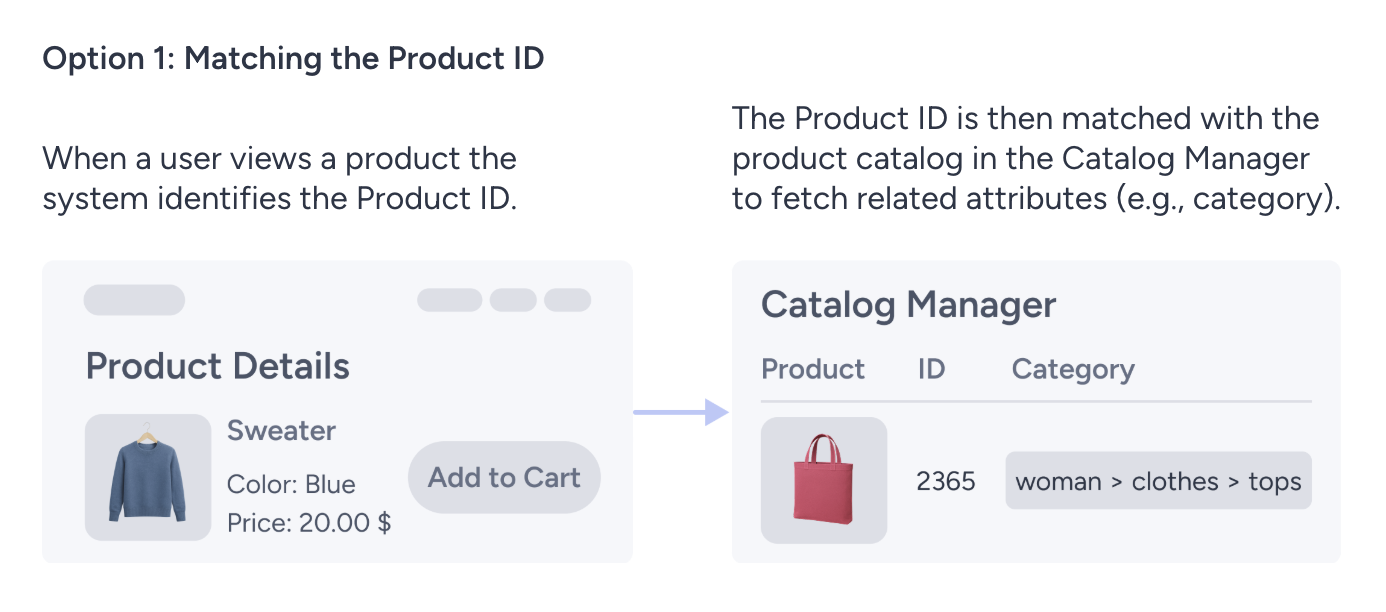
Product ID Matching
Dynamic values are retrieved based on the Product ID of the item the user is currently viewing. The required attribute value is derived from the product catalog using the Product ID collected from the viewed product.
If your dynamic value configuration is set to System Rules, default product attributes cannot be used in dynamic filters.
Real-life example
Suppose you want to create a recommendation campaign on product pages that displays the Most Popular items in the same color as the product a visitor is currently viewing.
To achieve this, you create a recommendation strategy with the filter Color + matches the item they’re currently viewing.
If your configuration uses System Rules, the color value is retrieved directly from the getCurrentProduct() rule on your website. Recommendations are then filtered based on that color. If the color value on your site does not match any value in the product catalog, no products will be returned.
If your dynamic value configuration uses Product ID Matching, the process works differently. First, the Product ID of the item the visitor is currently viewing is collected from your website. Then, the corresponding color value is retrieved from the product catalog using that Product ID. Recommendations are filtered using this catalog-based color value.