You can use the Wait For Action when you want to control the assistant behavior from your external system. This guide aims to explain how to use Wait For Action in your conversation flows, how Wait For Action works, and the use cases of Wait For Action.
- To add Wait For Action to your flow, drag and drop it from the Actions menu to your canvas or click on it.
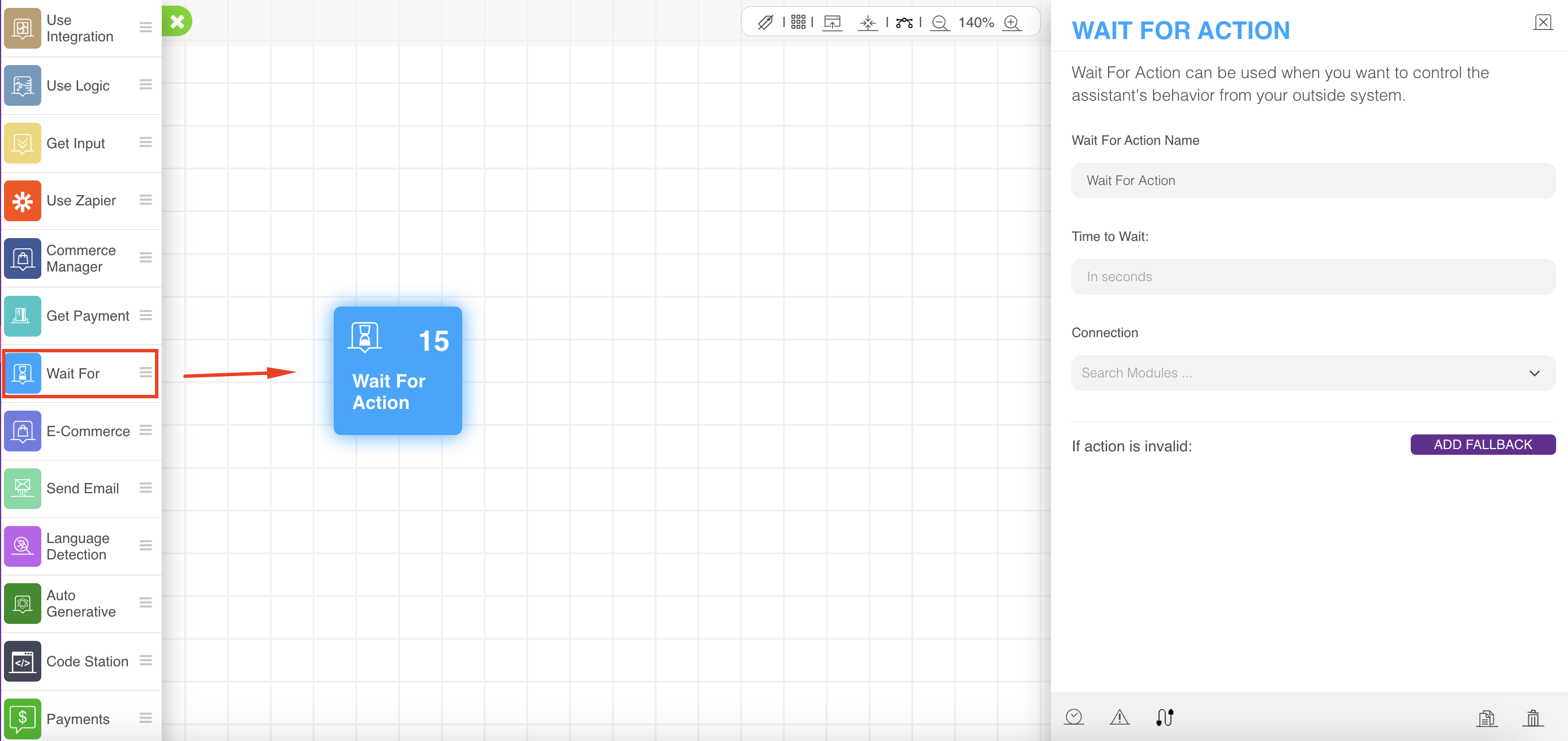
- Click on the action to configure the required parameters. You should define a timeout, the connection of the next coming action, and add a fallback action.
- After the timeout finishes, the action falls back automatically. A message should be received from outside to push the bot to continue.
- If the fallback is configured with some trials, the action will keep sending an error message for any user input until the trials are finished, then the action will fall back.
How does the Wait For Action work?
Wait for Action waits for a specific type of message "THIRDPARTY" and displays an error message for other types of messages until fallback. You can send a message from your system outside to our system using the following information:
| Messaging URL | https://app.MindBehind.com/external/v1/conversation/<Your channel id>/send |
| HTTP Method | POST |
| Required Header | “apiToken” that can be generated after creating the channel" |
| Body | It should be in JSON format with the following schema:
|
The flow will continue using the action connection as usual. In the case of the fallback set to true, the action will fall back. Also, after the timeout passes, the action will fall back passively through the incoming "THIRDPARTY" message with fallback being set to true.
Use Cases of Wait For Action
You can see a sample use case for shipment and same-day delivery below. Let's say you want to ask your users for their feedback about same-day grocery delivery. In this case, a sample flow would be as follows:
- MindBehind lists products.
- The user picks what to buy and sends a message.
- MindBehind handles transactions via payment action.
- MindBehind waits for an action from your store to send the user information about the delivery.
- Wait for Action gets triggered when an HTTP request is received.
- Received HTTP request with parameters explaining that the order shipped successfully.
- MindBehind sends a message to the end-user with parameters belonging to information about finalized delivery such as the delivery guy's name and delivery. Finalization date-time that is gathered from the HTTP request. (Refer to How does the Wait For Action work? for further details.)
- MindBehind asks the end-user to rate the delivery service.
- The user rates delivery service via message.
- The conversation ends.
- If an HTTP request is received with some parameters explaining that the order was canceled for some reason;
- MindBehind sends the end-user a message that says: "The delivery is canceled for some reason, that product is out of stock and the amount has been refunded from the store side".
- MindBehind returns the conversation to Step 4 again or ends the conversation according to the user input.
- If Wait For Action gets a timeout, it means a fallback without parameters specifying the reason behind that.
- MindBehind sends a message to the end-user that says "Sorry for being late".
- MindBehind sends an HTTP request to the delivery service API to check the delivery status and leave a warning alarm regarding the delivery via the integration module.
- MindBehind sends messages to end-users about the current status of delivery considering data that is gathered from the integration module.
- MindBehind returns the conversation to 4th action.
You can see an example of the best scenario for the use case below:
- Order gets delivered until the "Wait for third party module" gets a timeout.
- In Step 4, the delivery guy is expected to bring goods to the end-user and click the Finalize delivery button on his application.
- The Finalize delivery button executes an HTTP request (Step 6) to MindBehind to trigger the Wait For Action module with some parameters such as the delivery guy's name and delivery finalization date-time.
- Whenever the Wait For Action module receives the HTTP request, the bot might move further with gathered parameters from the received HTTP request (Step 7).
- At this point, the Wait For Action module completes its job. You can proceed with the required-desired scenario as in Steps 8,9 and 10.