You cannot make any changes to External Platform Integrations without having either an Administrator or an Editor with PII access in InOne. Refer to User Roles for further information.
This guide explains how to share user and event data from your Snowflake account to Insider One using Snowflake. This method ensures a secure, efficient pipeline that minimizes maintenance and overhead costs.
Essentials before integration
Before you begin, ensure the following prerequisites are met to ensure a smooth, secure data import from Snowflake to Insider One.
A Snowflake Enterprise or Business Critical account.
Permission to create and manage shares in Snowflake. The user setting up the share must have ACCOUNTADMIN access.
Access to the schema and tables that include user and event data.
Set up the Snowflake integration
If you want to integrate more than one Snowflake account into the same Insider One panel, please reach out to the Insider One team.
Follow the steps below to authenticate your Snowflake account and set up your data sync.
Navigate to InOne > Components > Integrations > External Integrations.
.png)
Click on the Snowflake integration.

Enter a name for your Snowflake source integration and click Save.
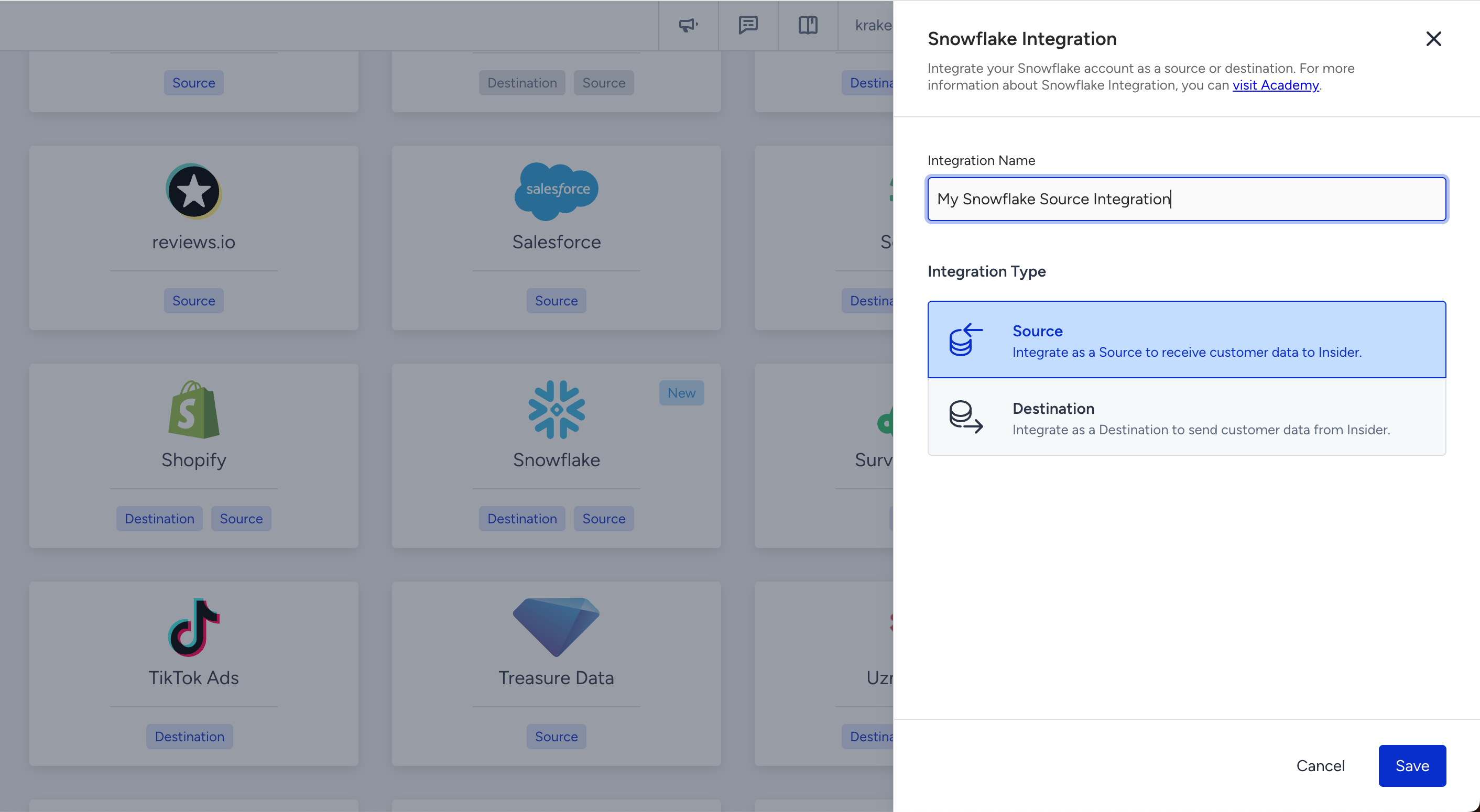
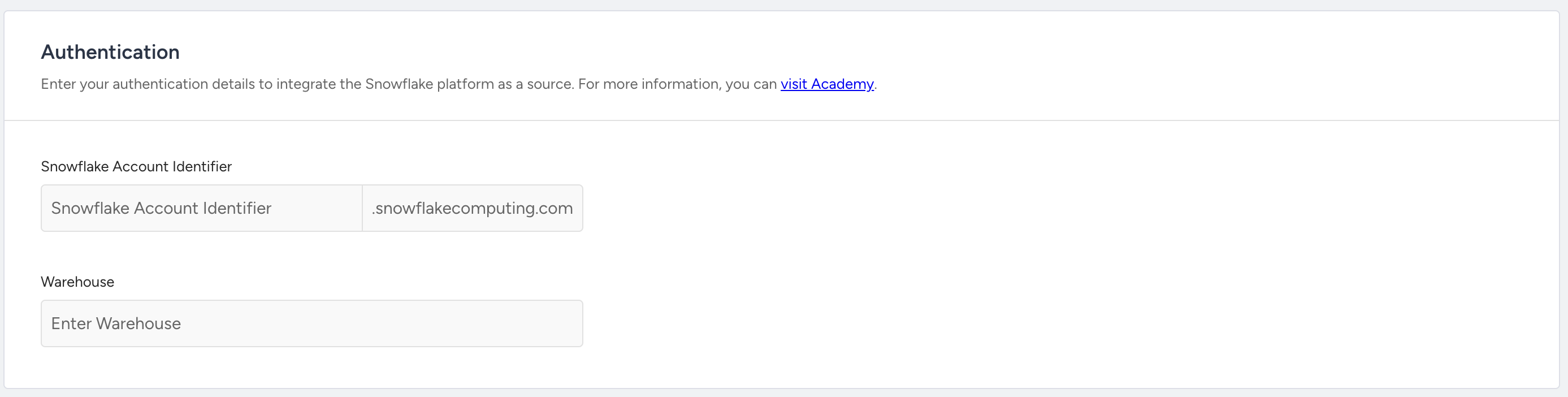
Enter your Snowflake Account Identifier and Warehouse Name.
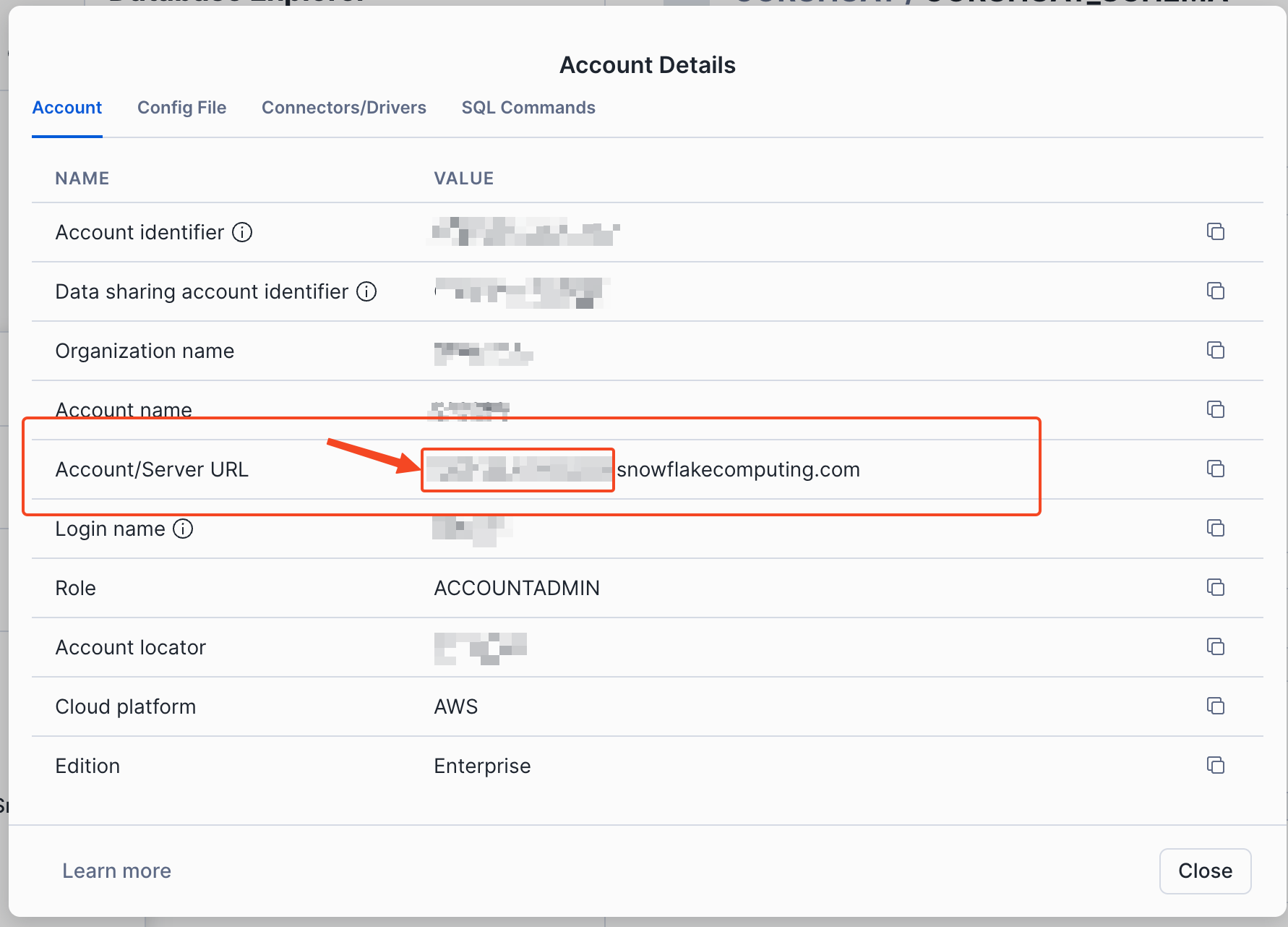
To find your Snowflake Account Identifier, go to Snowflake > Account Details and copy the first part of the Account/Server URL.
To get your Warehouse name, go to Snowflake > Compute > Warehouses and enter the Warehouse name that you want Insider One to use.
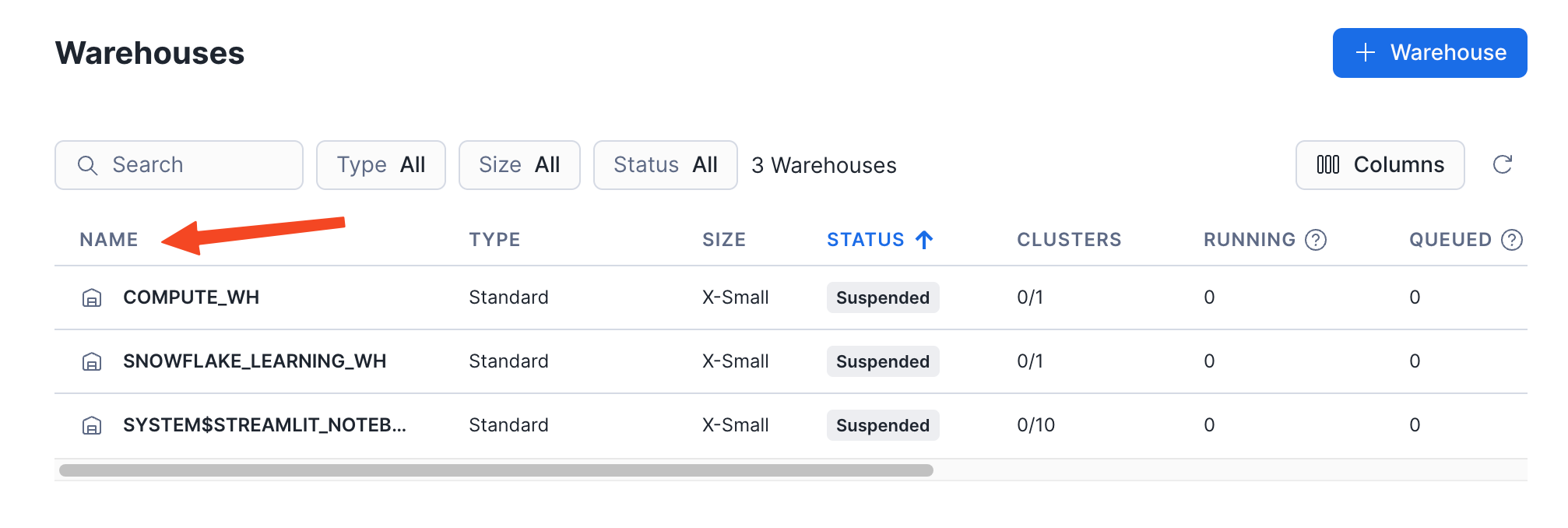
The size of the warehouse determines throughput. For large, initial loads (where you have a high volume of data), we advise to scale up the warehouse to maximize parallel processing and achieve the fastest possible ingestion time
Be sure that you add the IPs below to the IP white list in your Snowflake Account:
54.75.24.135
3.248.74.75
99.80.200.102
After you enter the Authentication inputs, scroll down to Script and Key Setup.
To create a Private Key and a Public Key, run the script below on your local machine terminal. Then, two files will be created.
openssl genrsa 2048 | openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -inform PEM -out rsa_key.p8 -nocrypt openssl rsa -in rsa_key.p8 -pubout -out rsa_key.pub
Upload this file:
rsa_key.p8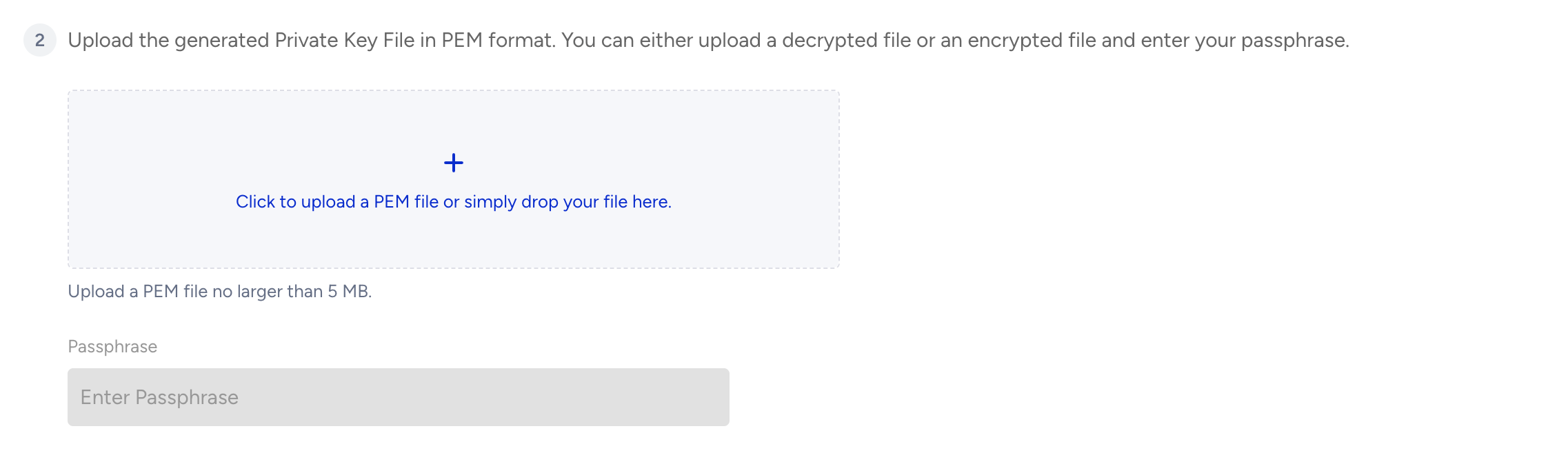
If you create with a different command in the terminal, which creates a private key with a Passphrase, you can use the Enter Passphrase input field. If your file requires a passphrase, the input field will automatically open.
Run an SQL in Snowflake. Make sure you replace the
<DB>,<SCHEMA>,<STREAM>and<PUBLIC KEY>placeholders with your actual values.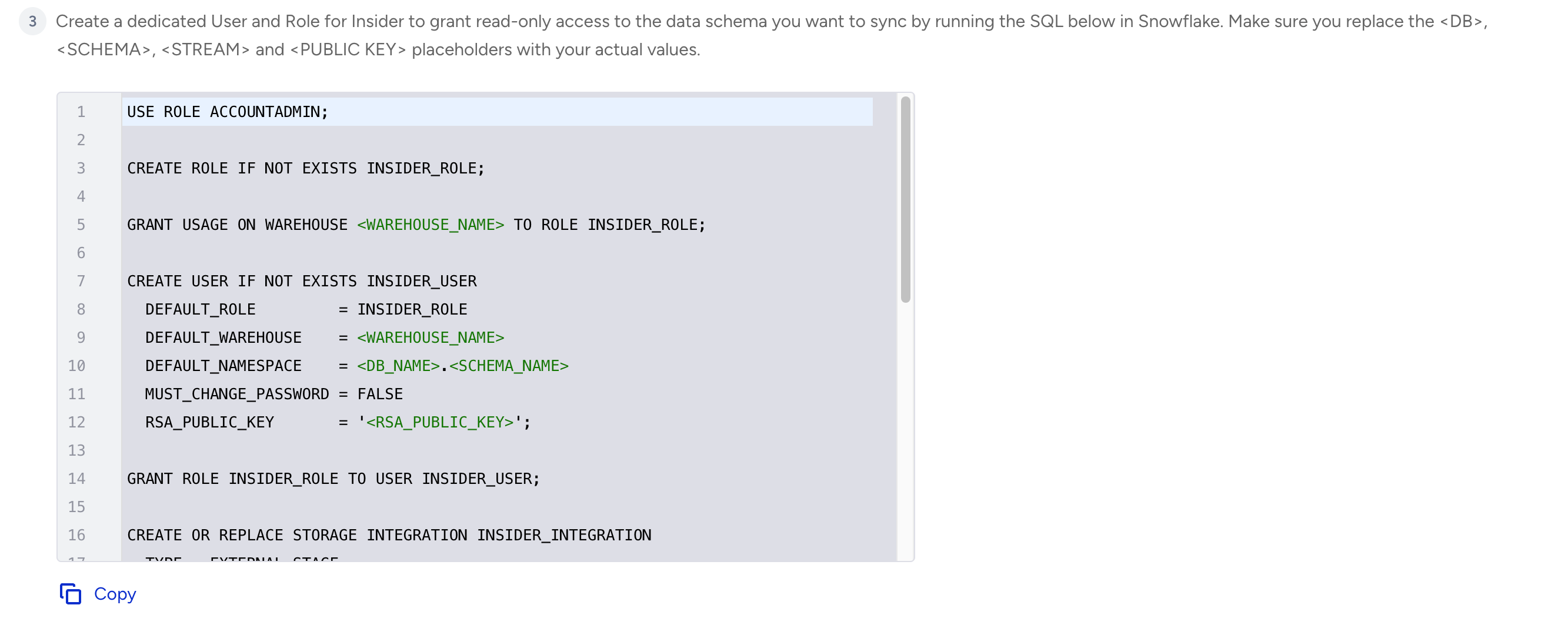
Copy the SQL from the InOne panel; each SQL is prepared according to the panel.
Important:
When replacing
<RSA_PUBLIC_KEY>, use only the raw key value. Do not include the lines:
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----You should paste only the actual key content, for example:
ABCDE1235…
Important:
Please do not modify any values in the SQL query except those enclosed in
< >. For example, the default user role should remainInsider_Role.
Important:
The Stream you grant to Insider One must be dedicated exclusively to Insider One and must not be used by any other integration or system. If another system also uses this Stream, Insider One will not be able to retrieve the all changes from Snowflake .
If you haven’t yet created a Stream for the table you are sharing with Insider One, refer to Snowflake documentation to create a dedicated Stream for Insider One.
Insider One automatically selects the Stream associated with a table. Therefore, the table you want to sync should only have one Stream, and that Stream must be the one created specifically for Insider One.
After you run all the SQL successfully in the Snowflake side, click the Verify Authentication button to verify your authentication.
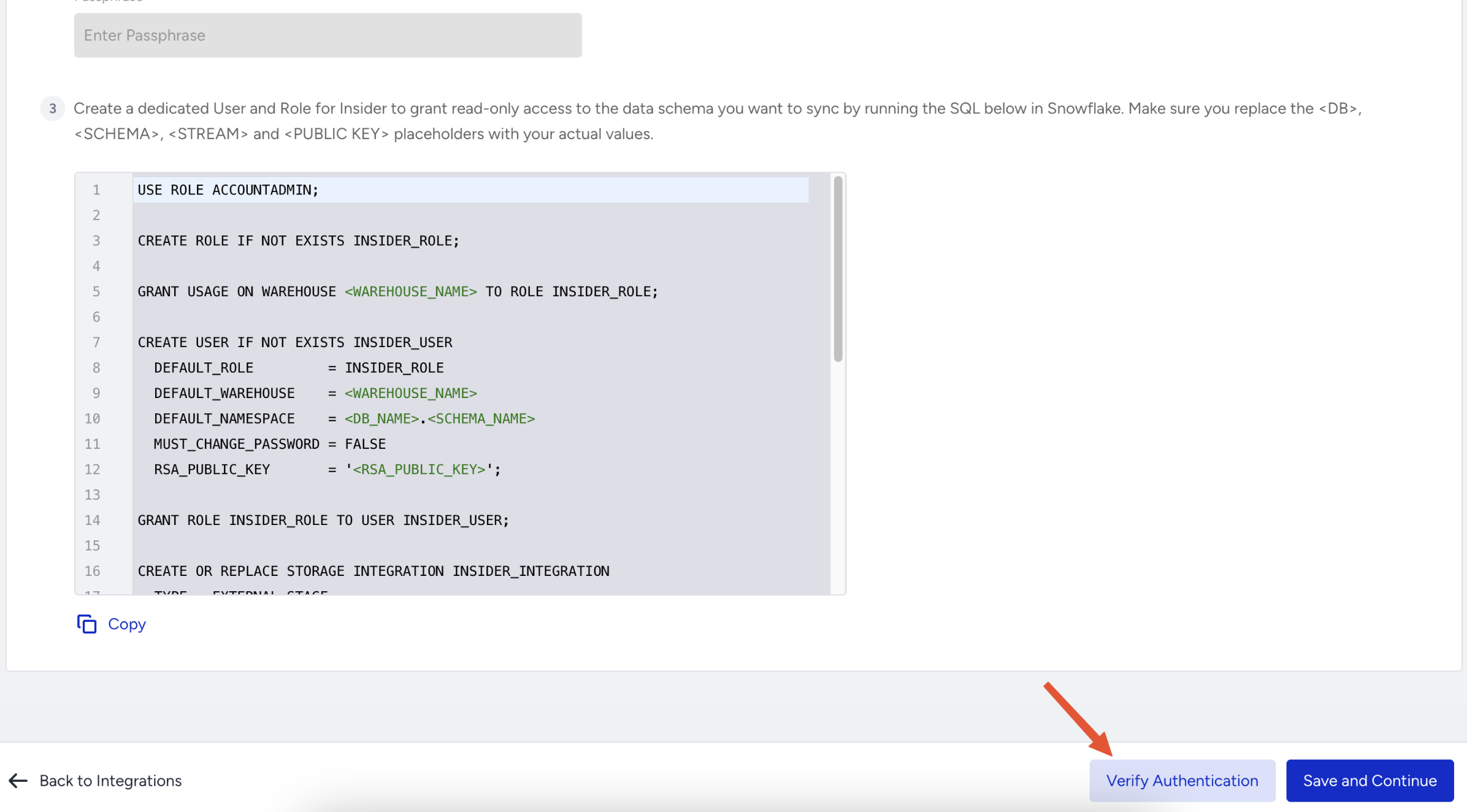
After verification, select the database, schema, and table you want to sync. If you’ve made any changes in Snowflake, click Refresh to load the latest structure.
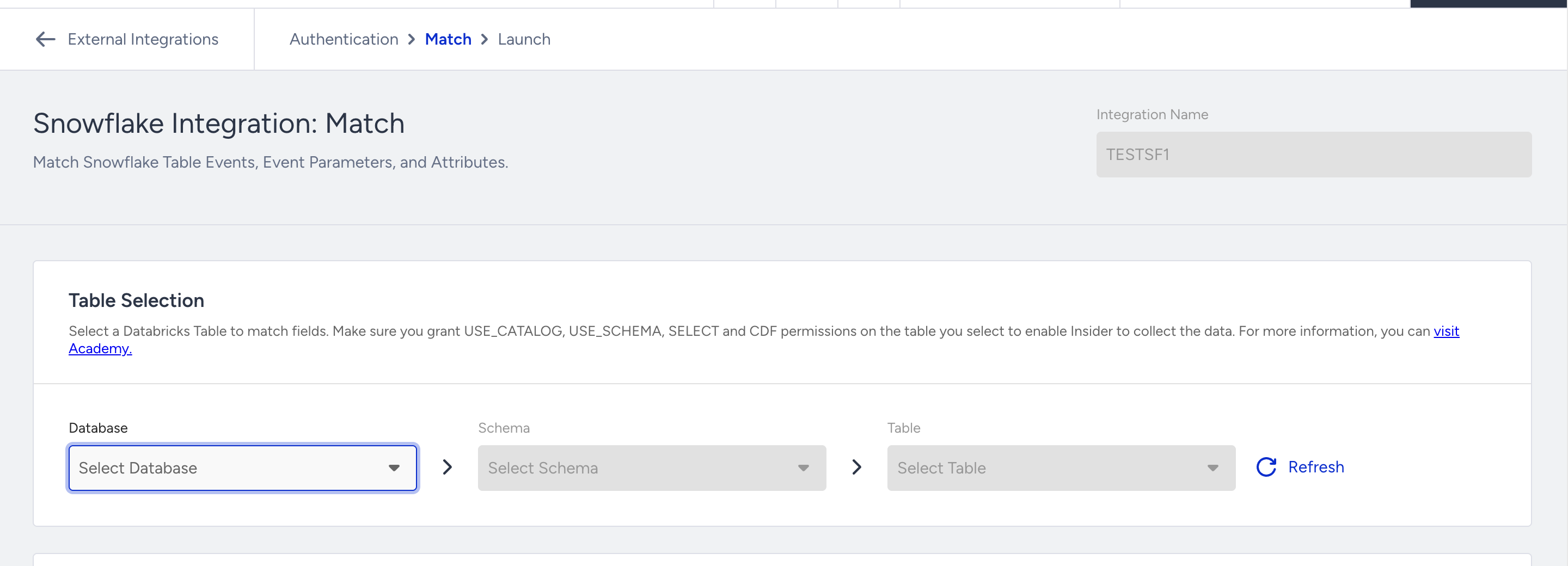
After selecting the table, you will be able to match the columns with Insider One’s attributes, events, and event parameters.
First, select the identifiers you want to send to Insider One. Data will be imported using the identifiers you choose. You may select more than one identifier. For example, if some of your users have only a phone number and others have only an email address, it is recommended to select both so that Insider One can match as many users as possible. However, it is essential to note that if the email or phone number for the same user in Insider One does not match the values you send from Snowflake, an identifier conflict will result.
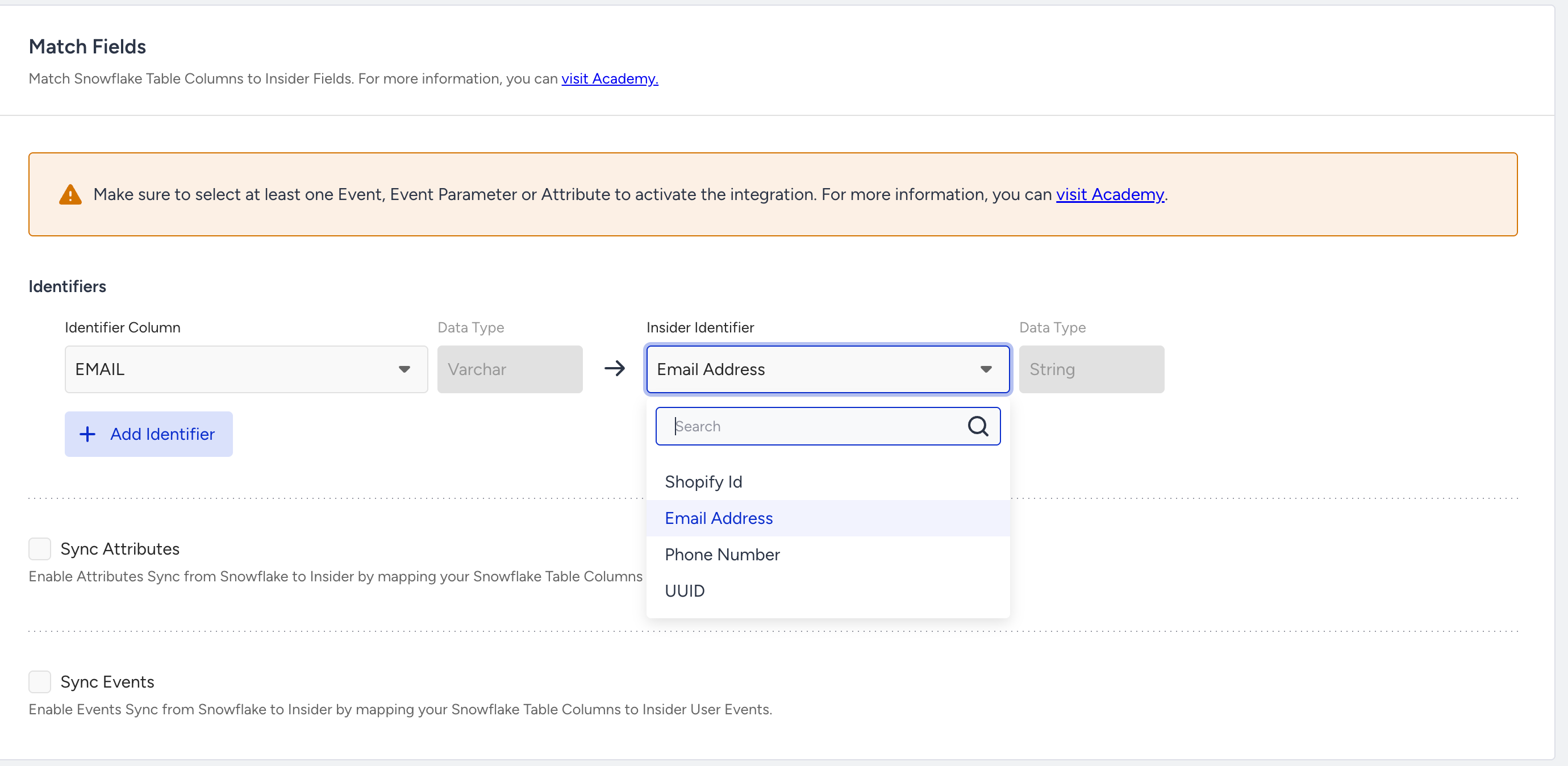
If you want to send attributes next to the identifier from Snowflake, you can open the Sync Attributes and map the columns in Snowflake to the Insider One Attributes.
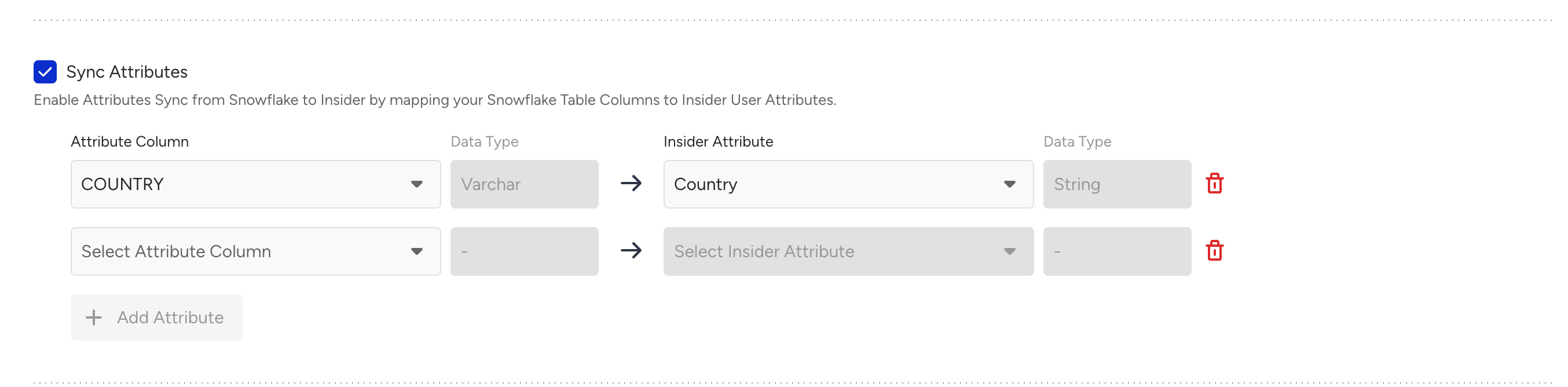
To map the Events and Event parameters from Snowflake, you can open Sync Events.
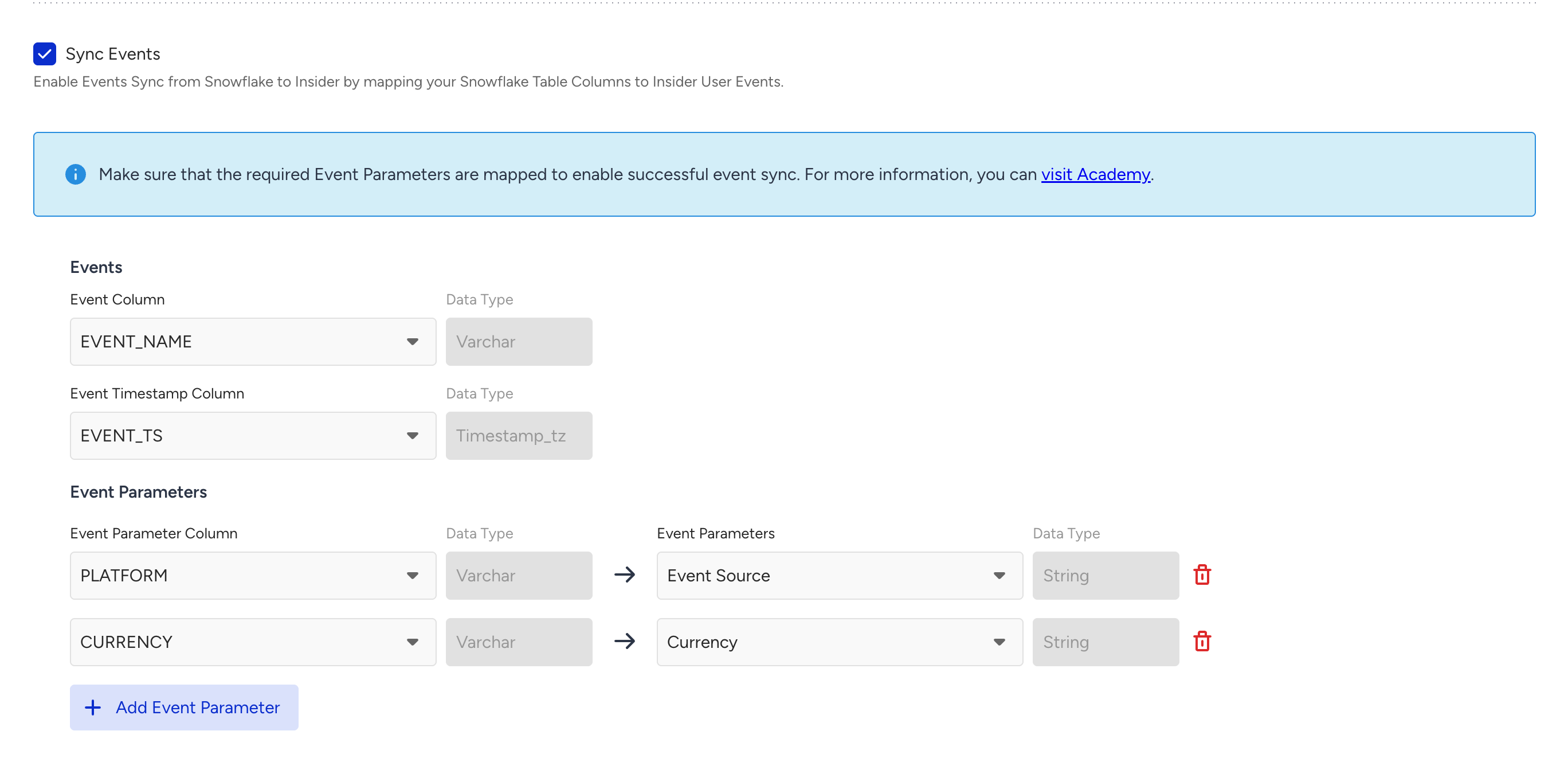
Refer to Default Attribute, Event & Parameter Data Mapping Table for required event parameters.
If you send events with the same name and timestamp, Insider One treats them as duplicates and ignores them. Therefore, avoid sending different events with identical names and timestamps.
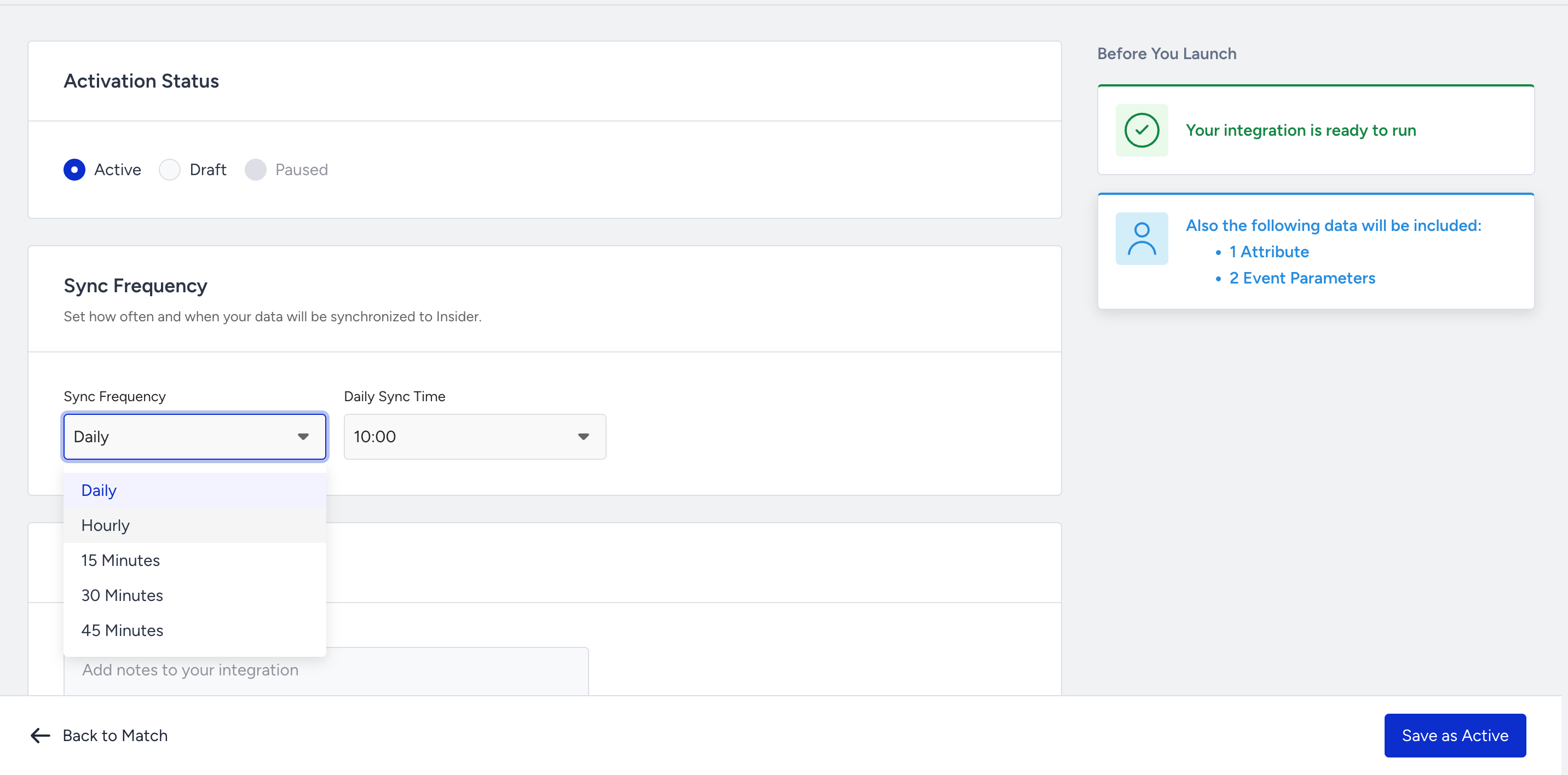
After completing the matching step, proceed to the Launch step. Choose how often you want the data to sync—every 15 minutes or up to once daily. Set the activation status to Active and click Save as Active.
Data Type Mapping
Ensure that the Insider One and Snowflake data types match. You can refer to the table below for data type matching:
Snowflake Data Type | Insider One Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
VARCHAR, TEXT | String | Used for text attributes, identifiers, and event parameters. |
NUMBER, INTEGER, DECIMAL, FLOAT | Number | Used for numerical attributes (e.g., a_age, e_quantity, e_unit_price). |
BOOLEAN | Boolean | Used for opt-in attributes (e.g., a_email_optin). |
TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP_LTZ, TIMESTAMP_NTZ, TIMESTAMP_TZ | DateTime | Insider One automatically converts any datetime format accepted by Snowflake. RFC3339 format is recommended for consistency. |
| Array Strings Array Numbers | Used for properties like |
Default Attribute, Event & Parameter Data Mapping Table
Parameter | Type | Description | Data Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Attribute | Attribute. The user’s email address can be used as an identifier. | String | No | |
phone_number | Attribute | Attribute. The user’s phone number in E.164 format (e.g., +6598765432) can be used as an identifier. | String | No |
email_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User’s permission for marketing emails: -True = emails allowed; -False = email not allowed | Boolean | No |
gdpr_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User’s permission for Insider One campaigns, data collection, and processing: -False = user will not see any Insider One campaign or receive any message from any channel; -True or empty = Insider One may interact with the user through personalization campaigns. | Boolean | No |
sms_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User’s permission for SMS: -True = SMS allowed; -False = SMS not allowed. | Boolean | No |
whatsapp_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User’s permission for WhatsApp Message: -True = WhatsApp Message allowed; -False = WhatsApp Message not allowed. | Boolean | No |
name | Attribute | Attribute. User’s name. | String | No |
surname | Attribute | Attribute. User’s surname. | String | No |
birthday | Attribute | Attribute. User’s birthday in RFC 3339 format (e.g. 1993-03-12T00:00:00Z). Note: Ensure the birthday ends with Z to indicate UTC time; no other time offset is included. Snowflake data type should be | Date/Time | No |
gender | Attribute | Attribute. Gender of the user. | String | No |
age | Attribute | Attribute. Age of the user. | Number | No |
language | Attribute | Language information of the user. | String | No |
country | Attribute | Attribute. The user’s country information in ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 format. | String | No |
city | Attribute | Attribute. City information of the user. | String | No |
uuid | Attribute | Attribute. The user’s UUID can be used as an identifier. | String | No |
event_name | Event | Name of the event. | String | Yes |
timestamp | Event Parameter | Event time. | Datetime | Yes |
event_group_id | Event Parameter | Event group ID. | String | No (Yes, only when the |
product_id | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Unique product ID. | String | No |
name | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Name of the product. | String | No |
taxonomy | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Category tree of the product. | Array | No |
currency | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Currency used for product pricing, in ISO 4217 format (e.g., USD). | String | No (Yes, only when the |
quantity | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Quantity of the product. | Integer | No (Yes, only when the |
unit_price | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Price of the product without any discount(s). | Float | No |
unit_sale_price | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Unit price of the product. | Float | No (Yes, only when the |
color | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Color of the product (selected by the user). | String | No |
size | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Size of the product (selected by user). | String | No |
shipping_cost | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Shipping cost of the items in the basket. | String | No |
promotion_name | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Name of the promotion. | String | No |
promotion_discount | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Total amount of discount applied by promotions. | Float | No |
Purchase Event
If you have purchase event in your Snowflake table, please make sure to;
If in a basket, there are more than single item, make sure to add those as seperated rows into your Snowflake table.
Include
e_guid(event_group_id) parameter for each purchase event. This is needed to connect different products to single cart.
Refer to Events & Attributes for all default events and attributes.
If your data type in Snowflake is a
TIMESTAMPformat, the specific date format is not critical. Insider One automatically converts any datetime format that is accepted by Snowflake.
Limitations
Each table must include an identifier.
Custom attributes or event parameters must be predefined in Insider One (see the Events & Attributes page).
For purchase events:
Add one row per product in a basket.
Include e_guid (event_group_id) to link multiple rows to a single cart.
Each row (user) must be under 5 MB; rows exceeding this limit will not be upserted.
Data Import Logic
During the Snowflake → Insider synchronization:
If any identifier coming from Snowflake is invalid, the entire record is not sent.
If an attribute coming from Snowflake is invalid, only that specific attribute is skipped.
If an event parameter coming from Snowflake is invalid, the entire event is excluded from processing.
The first synchronization performs a full table sync and doesn’t trigger any webhooks, campaigns, or journeys.
Important: Event Deduplication & Re-Ingestion Behavior
Duplicate Detection Rule: Insider One treats events with the same event name and timestamp as duplicates.
If multiple events with identical names and timestamps are sent within the same sync, only one will be processed and the others will be ignored.Avoid Updating Previously Synced Events: Do not update rows that were already consumed by Insider One in a previous sync.
Updating these rows triggers re-ingestion, which may create duplicate events in Insider.
Recommendation: Ensure each event has a unique timestamp and avoid modifying rows which include historical event records after they have been successfully synced.
Local Region Support
If your UCD uses a local region other than the default Ireland region, the integration will automatically use that region.
To change it later, contact the Insider One team.
FAQ
Q: Do I need to be on a specific Snowflake plan?
A: Yes, either Enterprise or Business Critical.
Q: What permissions are required in Snowflake?
A: You must have ACCOUNTADMIN privileges and access to relevant schemas and tables.
Q: Can Insider One access data in a different region?
A: Yes, but you need to enable cross-region replication.
Q: Can I share multiple tables with Insider One?
A: Yes, you can share multiple tables with Insider One.
Q: What happens if I include custom attributes or events?
A: They must be created first in Insider One’s Events & Attributes page and mapped in the Match page.
Q: Can I send purchase events with multiple products?
A: Yes. Add each product as a separate row and use the event_group_id (e_guid) to link them to the same cart.
Q: How should I format dates (like a_birthday and e_timestamp)?
A: If your data type in Snowflake is a TIMESTAMP format, the specific date format is not critical. Insider One automatically converts any datetime format that Snowflake accepts. For example, 1993-03-12T00:00:00Z is a valid RFC3339 format, but Insider One can also process other standard Snowflake datetime formats.
Q: How can I delete a user attribute or an entire user profile?
A: The Snowflake integration performs data synchronization based on updates and additions. It does not support explicit "delete" operations for user attributes or entire user profiles within Insider One. If a record is deleted in your Snowflake table, it will not automatically trigger the removal of that data from Insider One during the next sync. To delete user data in Insider One, you can use Insider One's dedicated user deletion features or contact Insider One team.
Q: Under what conditions does a Snowflake stream become “stale”?
A: A stream becomes stale when its “offset” falls outside the data-retention period of its source table (or underlying tables for a view). At that point, historical data — including any unconsumed change records — is no longer accessible, and you must recreate the stream to resume change capture. Refer to Snowflake’s documentation for more information.