RFM stands for recency, frequency, and monetary value. This method analyzes a user's past transaction data, creates different segment groups based on their purchase history, and measures the customer value. 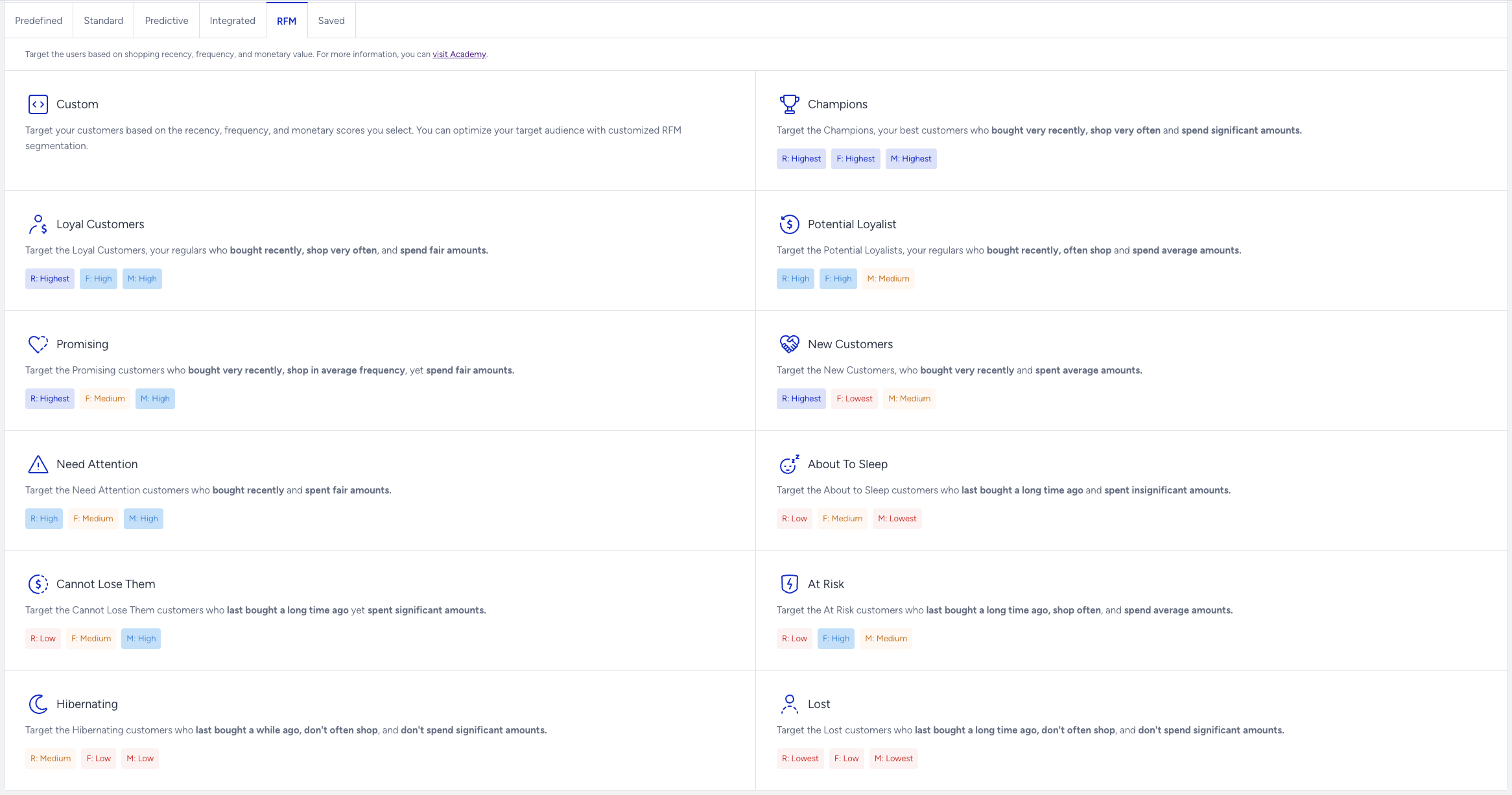
The available segments of RFM might vary depending on the product you are using.
Scoring Model
Five levels of scores are available for Recency, Frequency, and Monetary values (scores 1–5).
Total possible combinations: 125 segments (5³)
Score interpretation
5 = Highest ranking (e.g., most recent activity, highest frequency, highest spending)
1 = Lowest ranking (e.g., long inactive, low frequency, low spending)
Definitions
Recency: Time since last purchase or activity with the brand.
Frequency: How often purchases or interactions occur with the brand during a particular period.
Monetary: How much a user spends during a defined period
Calculation Basis
Ecommerce websites: RFM is calculated based on purchases.
Non-ecommerce websites: RFM is calculated based on sessions.
RFM Segment Requirements
Data used: Only purchase behavior is used for segmentation (app, web, CRM). Behavioral data, like session views or product interactions, is not considered.
Segment update frequency: Segments are updated daily. A customer’s segment can change daily based on their latest purchase activity.
Data span: Up to 12 months of purchase history is processed when calculating segments.
Use Cases
RFM scores can help identify and engage a variety of customer segments:
High-spending new customers: Score high on recency and monetary, but low on frequency.
Frequent low spenders: Score high on frequency, but low on monetary value.
One-time big spenders: Purchased only once, but spent above average.
VIP customers: Score high across all three dimensions.
High-value churn risks: Score high on frequency and monetary, but low on recency.
Low-value customers: Score low across recency, frequency, and monetary value.