You cannot make any changes to External Platform Integrations without having either an Administrator or an Editor with PII access in InOne. Refer to User Roles for further information.
This guide explains how to securely import user attribute and event data from your Google BigQuery (GBQ) tables into Insider One for advanced segmentation, targeting, and personalization.
Essentials before the integration
A Google Cloud project with BigQuery enabled.
Service account credentials (JSON key file) with the following IAM roles:
BigQuery Data Viewer
BigQuery Job User
BigQuery Metadata Viewer
Access to the datasets and tables containing user and event data.
A column (e.g.,
updated_at) in your table/view to track row updates for incremental sync.
Step 1: Create a Service Account
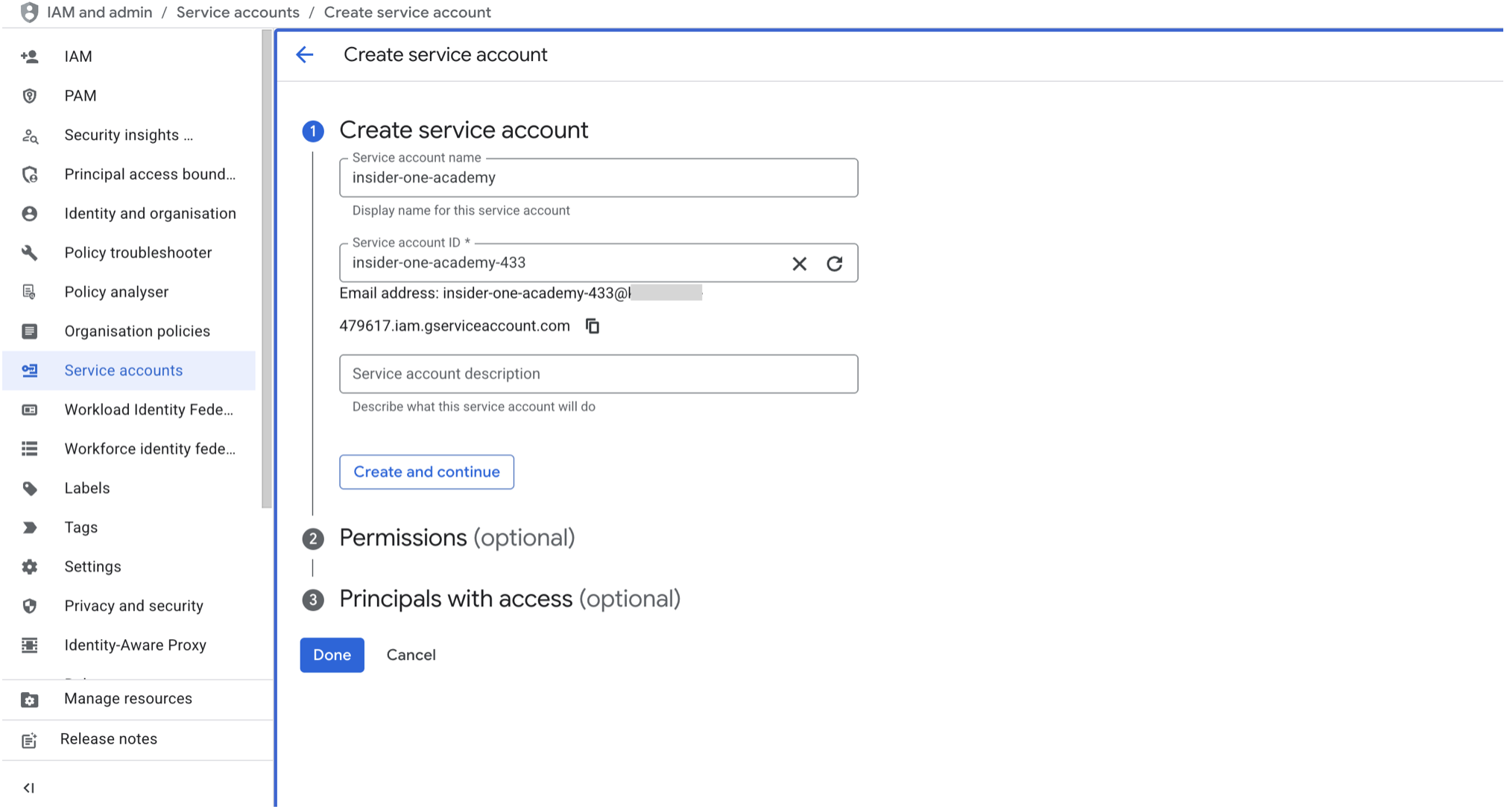
To create a Service Account, you should:
1.1. Go to the Google Cloud Console – Service Accounts page.
1.2. Select your project (from the top navigation bar).
1.3. Click Create Service Account.
1.4. Enter a name (e.g., insider-bigquery-integration) and description.
1.5. Click Create and Continue.
Refer to Google’s documentation for further details on creating and managing service accounts.
1.6. To assign required roles, add the following roles in the “Grant this service account access to project” step:
BigQuery Data Viewer (
roles/bigquery.dataViewer)BigQuery Job User (
roles/bigquery.jobUser)BigQuery Metadata Viewer (
roles/bigquery.metadataViewer)BigQuery Read Session User (
roles/bigquery.readSessionUser)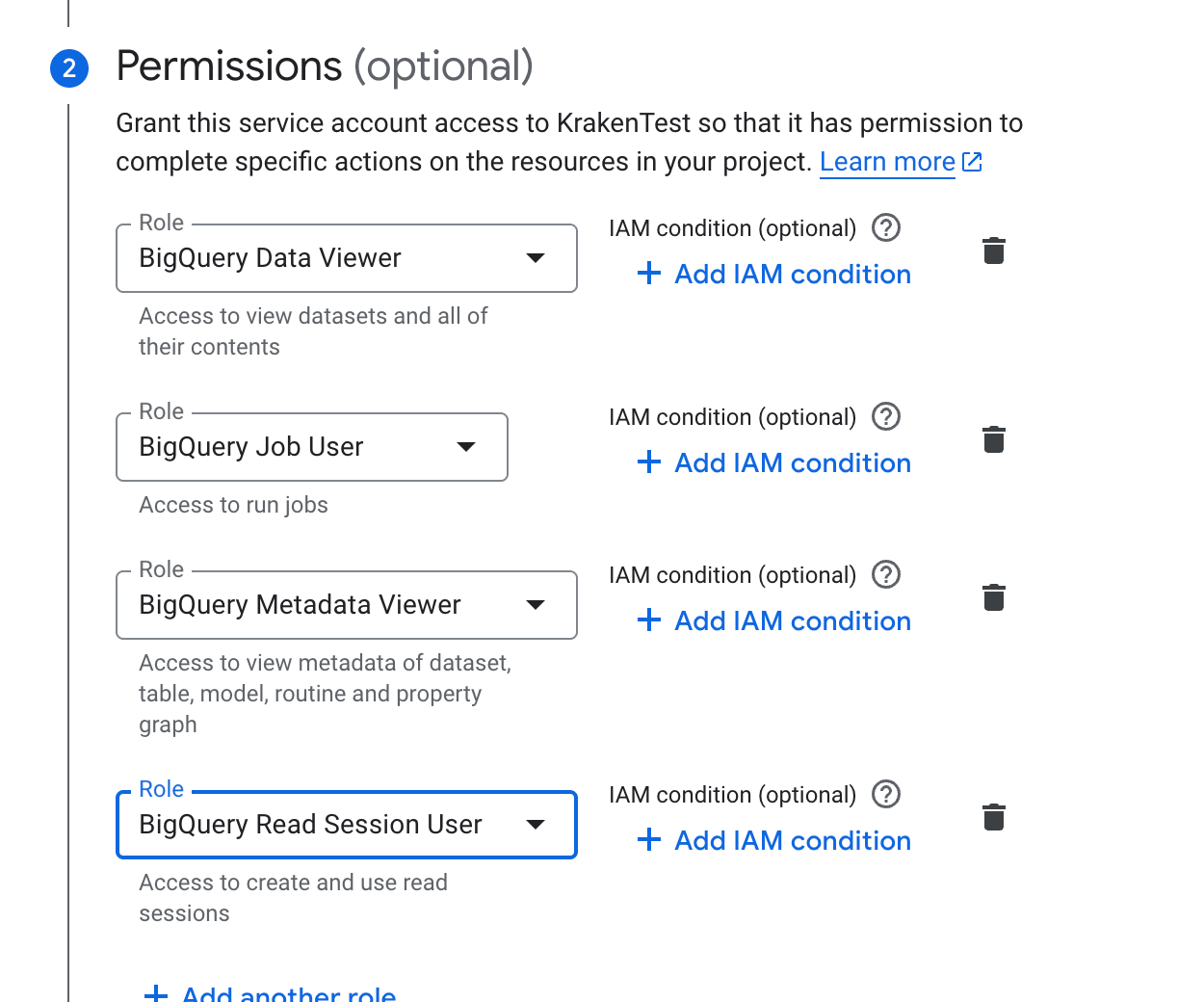
Refer to Google’s documentation for further details on BigQuery predefined IAM roles.
To finish and create the Service Account,
1.7. Click Done after adding the roles. Your service account will appear in the list.
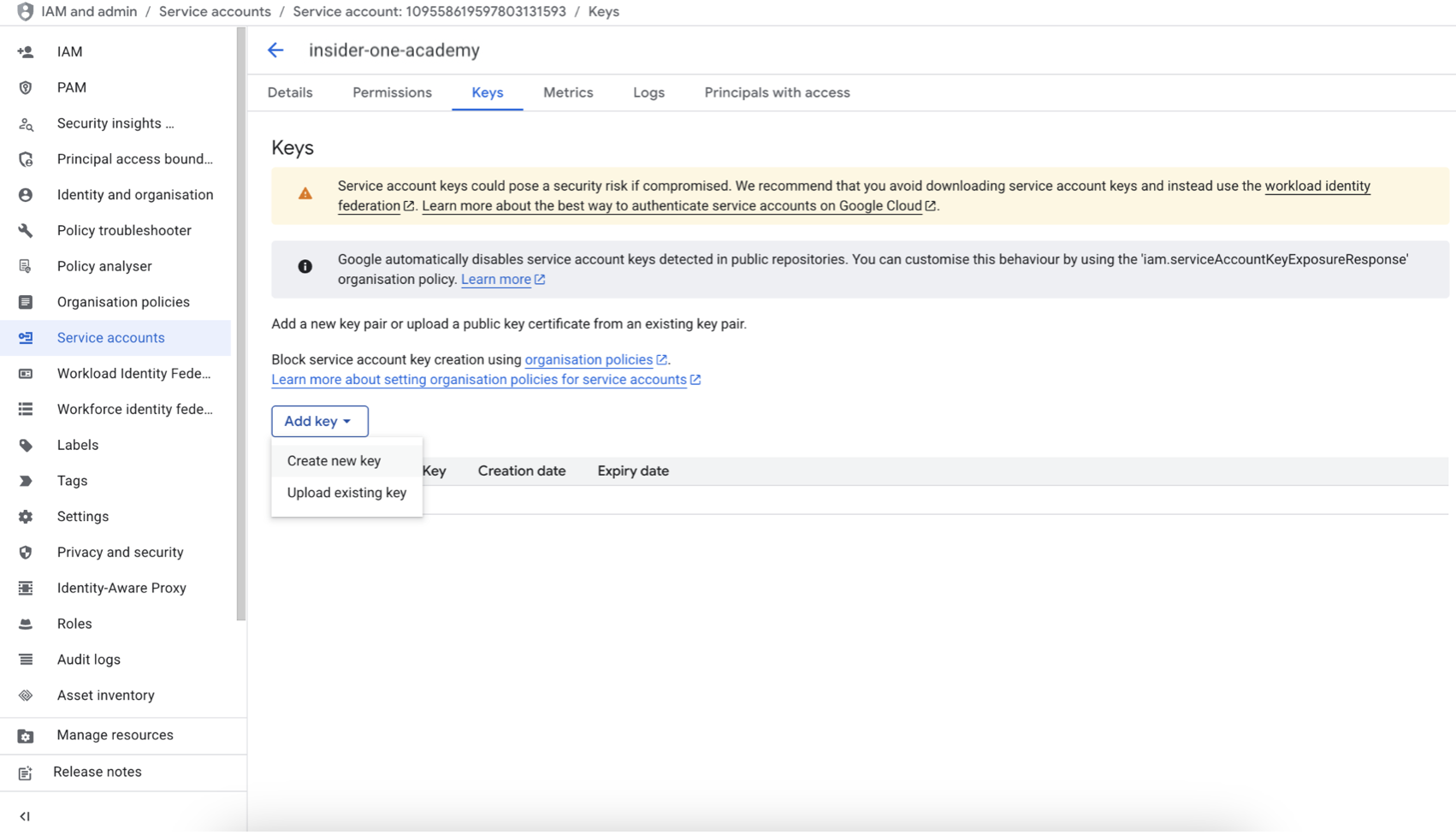
1.8. In the Service Accounts list, click the email of your new service account.
1.9. Go to the Keys tab.
1.10. Click Add Key > Create new key.
1.11. Select JSON and click Create.
The JSON key file will be downloaded automatically to your computer.
Refer to Google’s documentation for further details on creating and managing service accounts.
Step 2: Upload the JSON Key to Insider Console
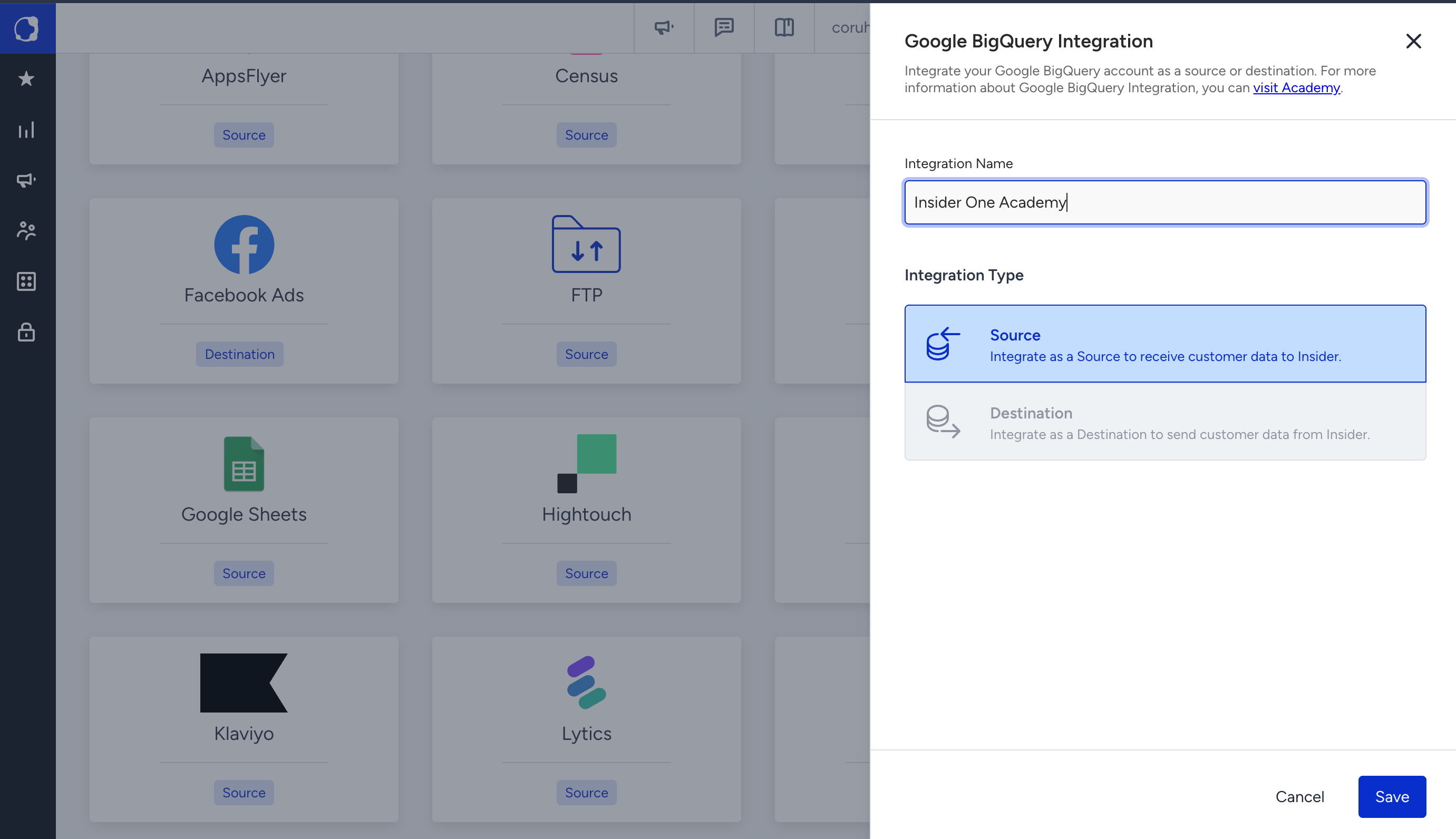
2.1. Navigate to Components > Integrations > External Integrations on the Insider One’s InOne panel. 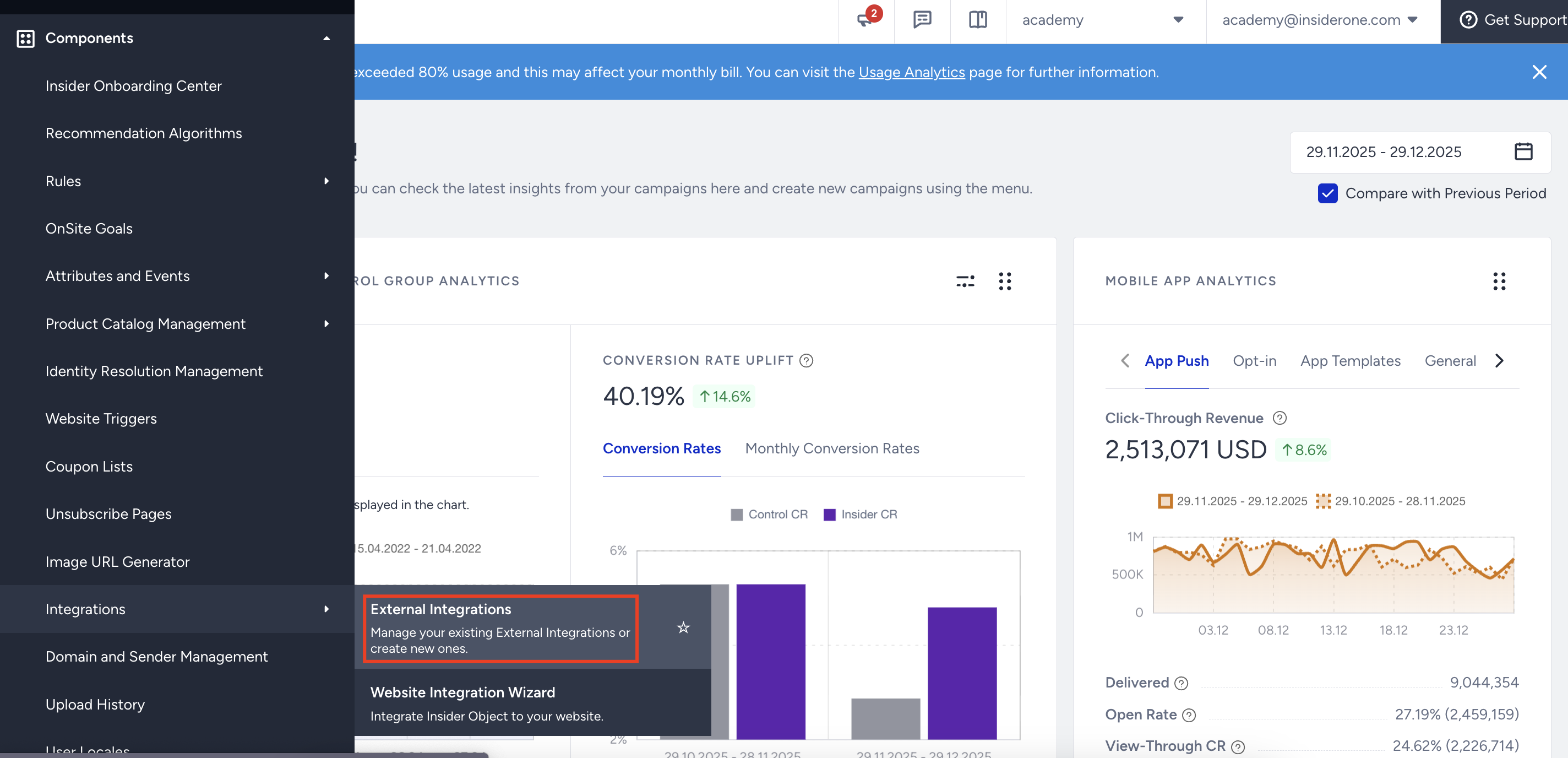
2.2. Select Google BigQuery integration.
2.3. Enter a name for your integration and click Save.
2.4. Click Upload Service Account Key and select the JSON file you downloaded in Step 1.11.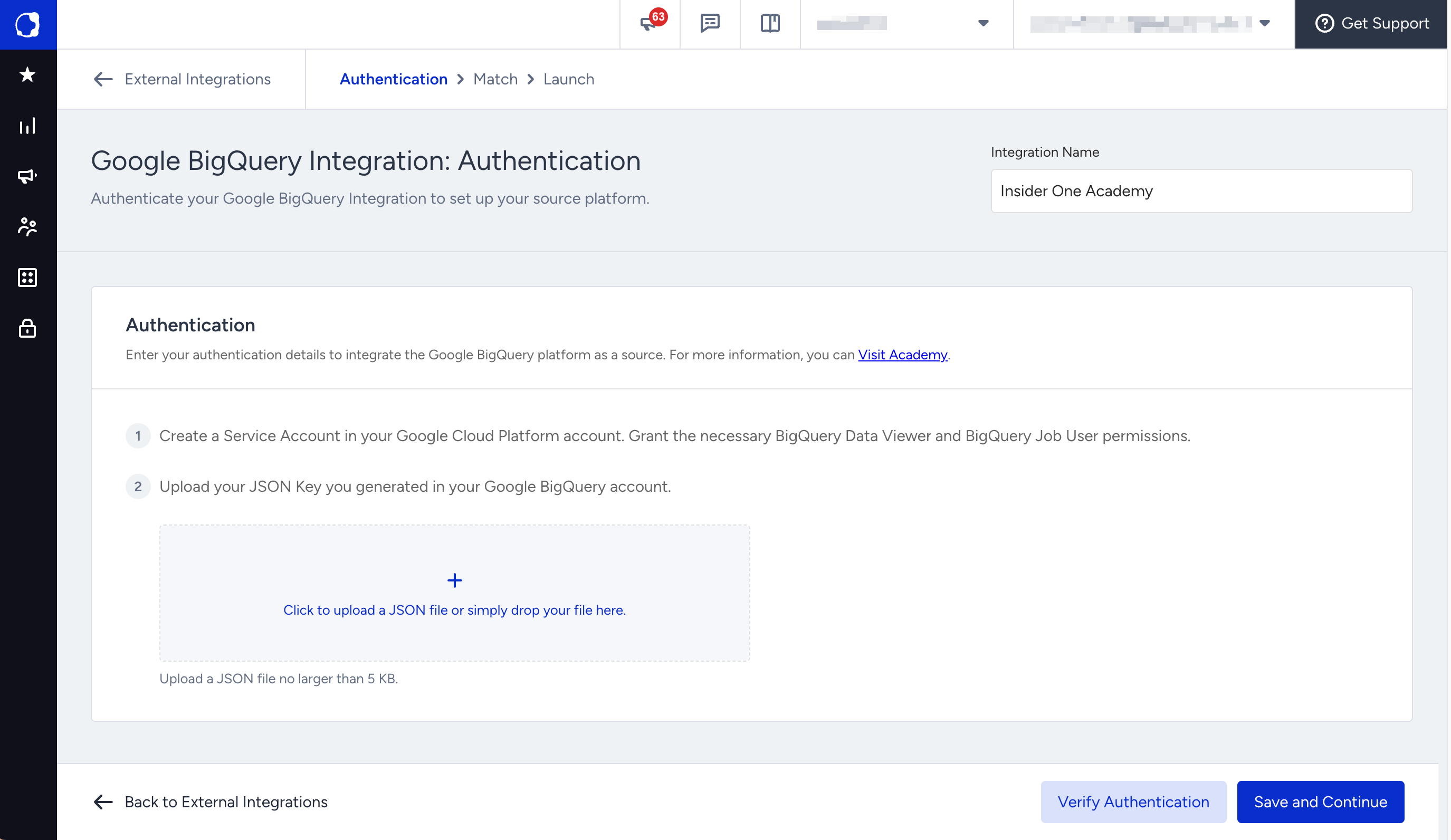
2.5. Click the Verify Authentication button to verify your Service Account. 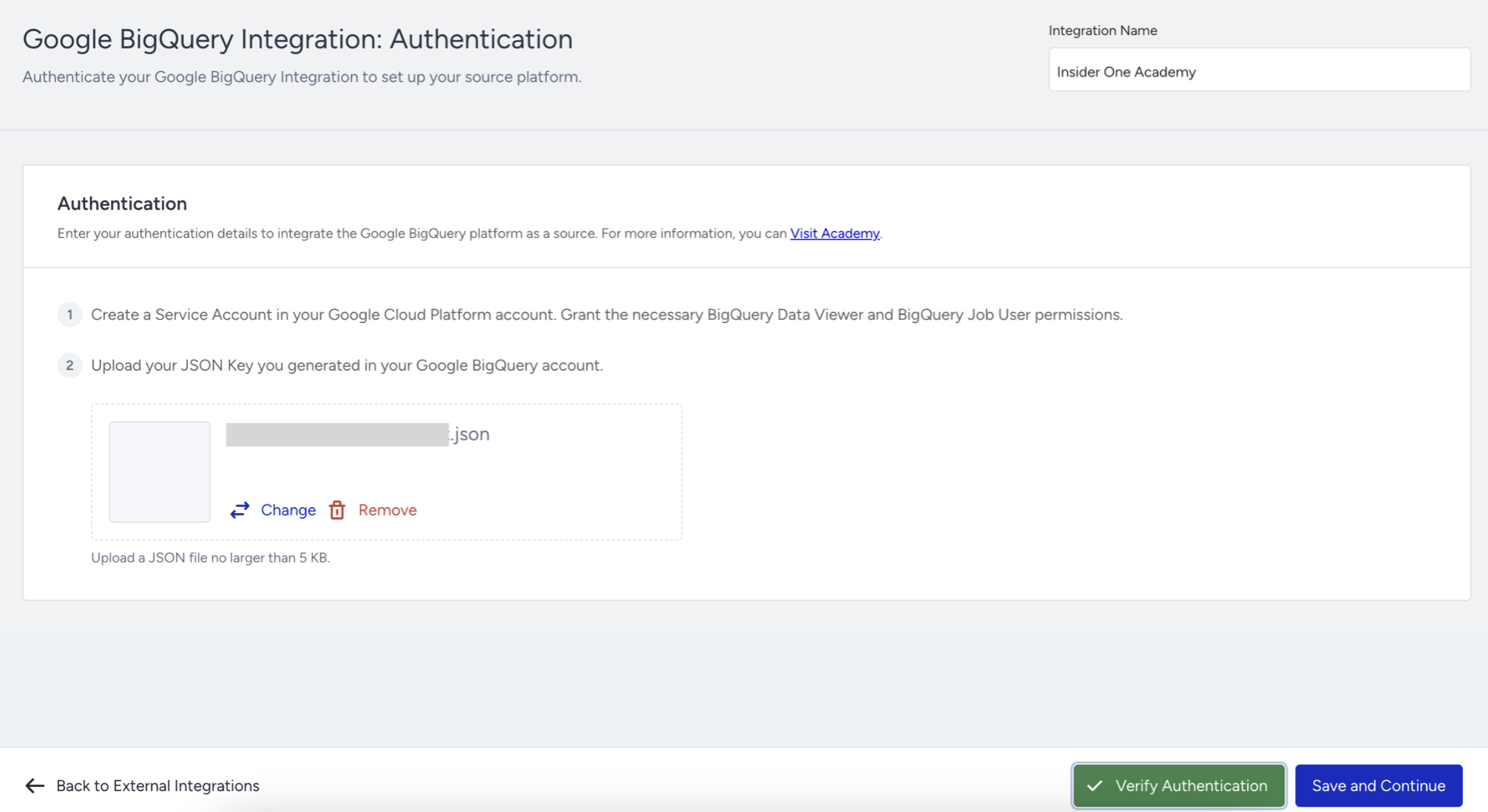
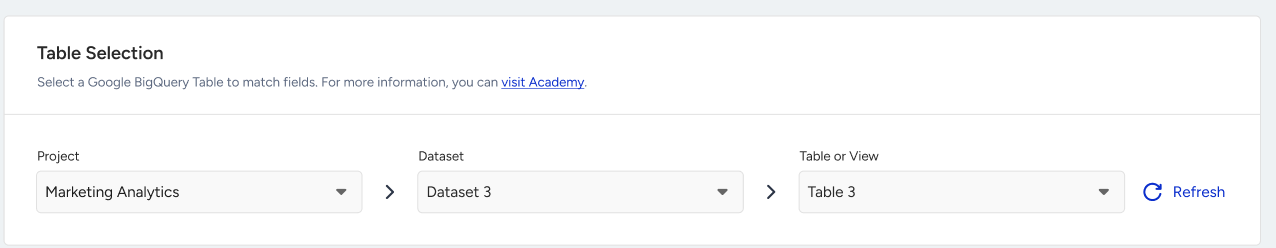
Step 3: Select Dataset and Table
After successful authentication, Insider One will display a list of available projects, BigQuery datasets, and tables in your project.
If you cannot find your dataset in here, you should check if you gave permission to that dataset or table while creating the Service Account.
3.1. Select the desired Dataset.
3.2. Choose the Table or View you want to import data from.
Step 4: Mapping GBQ Columns to Insider One Identifiers, Attributes, Events
4.1. You should map at least one identifier from GBQ to Insider One so that Insider One can understand which users you are sending data for.
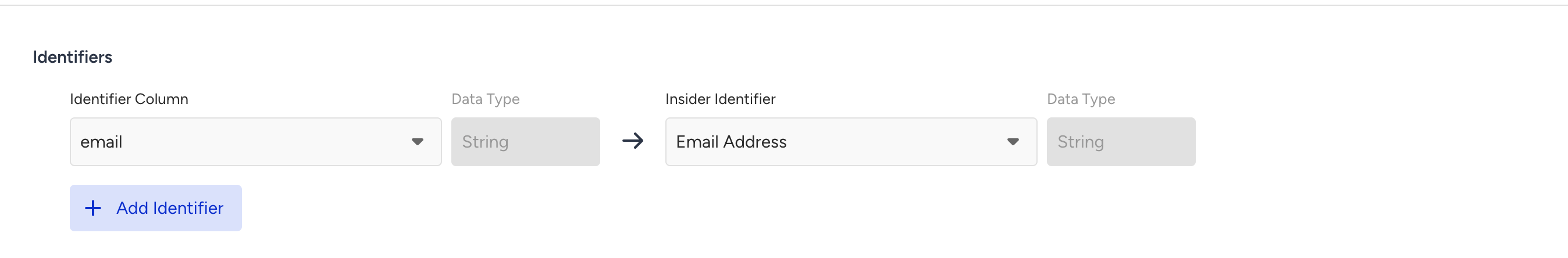
Only string can be mapped to the Insider One Identifiers.
4.2. After selecting the identifier, you should select the Last Updated Column so that Insider One can understand which rows are updated in each new sync.

Only timestamp data type can be selected as Last Updated Column
You should maintain that Last Updated Column properly so that it reflects the changes in order to have proper data sync between GBQ and Insider One.
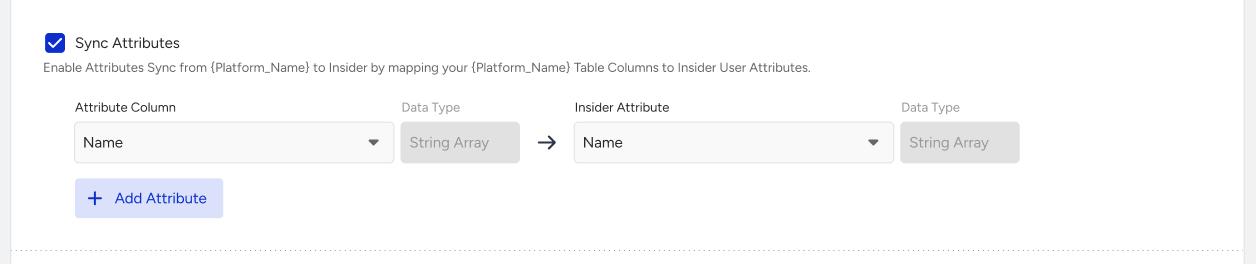
If you want to send data to Insider Attributes from GBQ, you should enable the Sync Attributes and map the columns to the Insider attributes.
If you want to sync events, enable the Sync Events.
Select the column that represents the event name in your table.
Select the column that represents the event timestamp in your table.
Select the column that represents event parameters in your table.
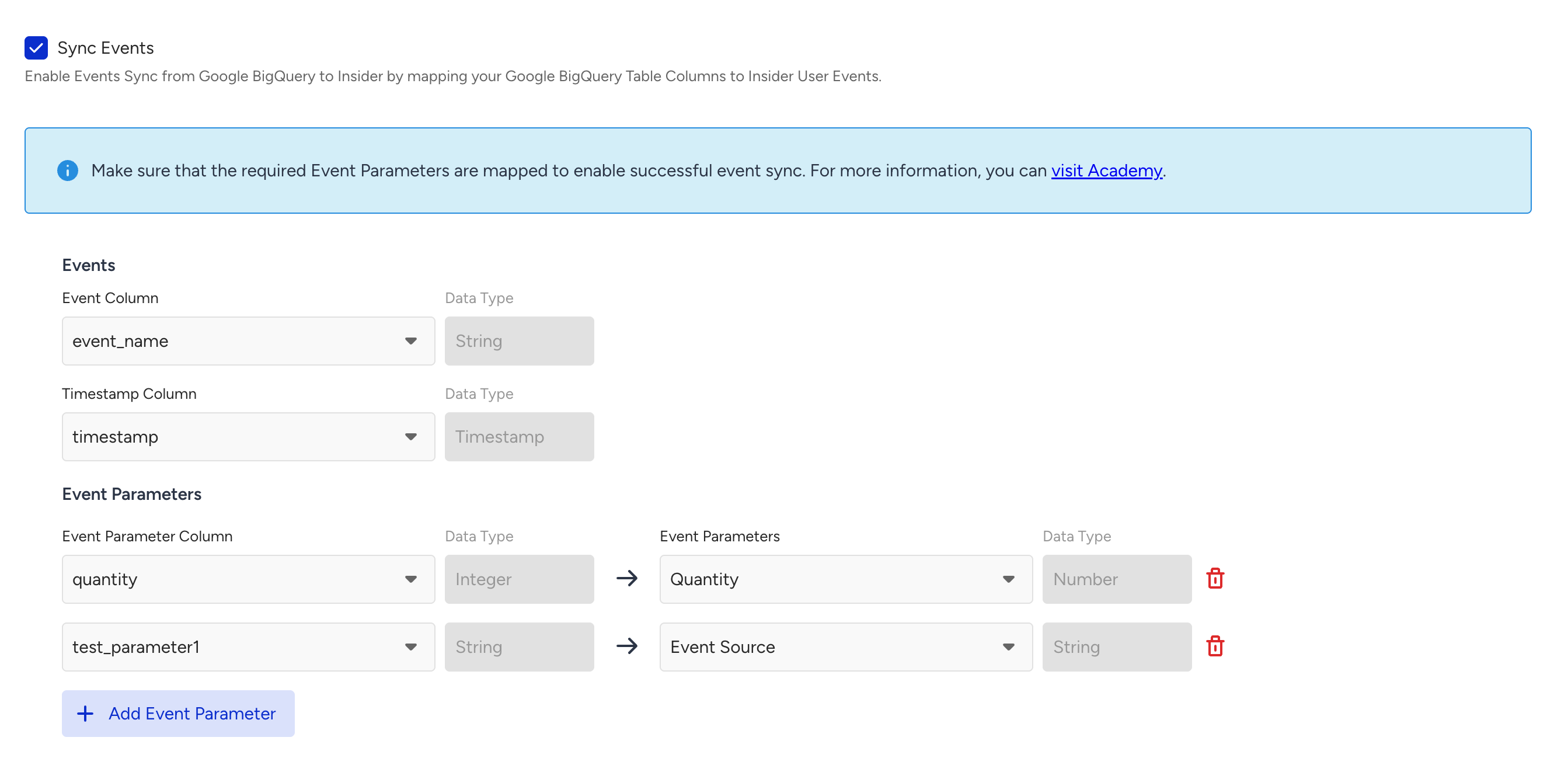
If you send events with the same name and timestamp, Insider One treats them as duplicates and ignores them. Therefore, avoid sending different events with identical names and timestamps.
Data Type Matching
Ensure that the Insider and Google BigQuery data types are matched. Below is the table for data type matching.
Google BigQuery Data Type | Insider Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
STRING | String | Used for text attributes, identifiers, and event parameters. |
INT64, FLOAT64, NUMERIC, BIGNUMERIC | Number | Used for numerical attributes (e.g., age, quantity, unit_price). |
BOOL | Boolean | Used for opt-in attributes (e.g., email_optin). |
TIMESTAMP, DATETIME, DATE | DateTime | Insider One auto-converts any datetime format accepted by BigQuery. RFC3339 recommended. |
ARRAY | Array Strings | Used for properties like taxonomy. Map string arrays to string arrays. |
ARRAY<NUMERIC/INT64/FLOAT64> | Array Numbers | Map number arrays to number arrays. |
Default Attribute, Event & Parameter Data Mapping table
Parameter | Type | Description | Data Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Attribute | Attribute. The user's email address can be used as an identifier. | String | No | |
phone_number | Attribute | Attribute. User's phone number in E.164 format (e.g. +6598765432), can be used as an identifier. | String | No |
email_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User's permission for marketing emails. | Boolean | No |
gdpr_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User's permission for Insider campaigns, data collection, and processing. | Boolean | No |
sms_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User's permission for SMS. True = SMS allowed; False = SMS not allowed. | Boolean | No |
whatsapp_optin | Attribute | Attribute. User's permission for WhatsApp Message. True = WhatsApp Message allowed; False = WhatsApp Message not allowed. | Boolean | No |
name | Attribute | Attribute. User's name. | String | No |
surname | Attribute | Attribute. User's surname. | String | No |
birthday | Attribute | Attribute. User's birthday in RFC 3339 format (e.g. 1993-03-12T00:00:00Z). | Date/Time | No |
gender | Attribute | Attribute. Gender of the user. | String | No |
age | Attribute | Attribute. Age of the user. | Number | No |
language | Attribute | Language information of the user. | String | No |
country | Attribute | Attribute. The user's country information in ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 format. | String | No |
city | Attribute | Attribute. City information of the user. | String | No |
uuid | Attribute | Attribute. The user’s UUID can be used as an identifier. | String | No |
event_name | Event | Name of the event. | String | Yes |
timestamp | Event Parameter | Event time. | Datetime | Yes |
event_group_id | Event Parameter | Event group ID. | String | No (Yes only when the event_name is purchase or cart_page_view) |
product_id | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Unique product ID. | String | No |
name | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Name of the product. | String | No |
taxonomy | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Category tree of the product. | Array | No |
currency | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Currency used for product pricing, in ISO 4217 format (e.g., USD). | String | No (Yes only when the event_name is purchase or cart_page_view) |
quantity | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Quantity of the product. | Integer | No (Yes, only when the event_name is purchase) |
unit_price | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Price of the product without any discount(s). | Float | No |
unit_sale_price | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Unit price of the product. | Float | No (Yes only when the event_name is purchase or cart_page_view) |
color | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Color of the product (selected by user). | String | No |
size | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Size of the product (selected by user). | String | No |
shipping_cost | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Shipping cost of the items in the basket. | String | No |
promotion_name | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Name of the promotion. | String | No |
promotion_discount | Event Parameter | Event parameter. Total amount of discount applied by promotions. | Float | No |
If you have purchase event in your Google BigQuery table, please make sure to;
If in a basket, there are more than single item, make sure to add those as seperated rows into your Google BigQuery table.
Include
e_guid(event_group_id) parameter for each purchase event. This is needed to connect different products to single cart
Refer to Events & Attributes for further information on all default events and attributes.
If your data type in Google BigQuery is a
TIMESTAMPformat, the specific date format is not critical. Insider One automatically converts any datetime format that is accepted by Databricks.
Step 5: Configure Sync Frequency and Launch
5.1. Choose how often Insider One should fetch data from GBQ. The options are 15 min, 30 min, 45 min, hourly, and daily.
When you activate the integration, Insider fetch all the data in that table or view without looking to Last Updated Column in order to make the full table sync. After full table sync Insider starts looking to Last Updated Column to get the latest updated rows.
5.2. Review your configuration and mappings.
5.3. Select Activate and click the Save as Active button to activate the integration.
During the first full table sync, you will not be able to change the settings and configurations of your integration.
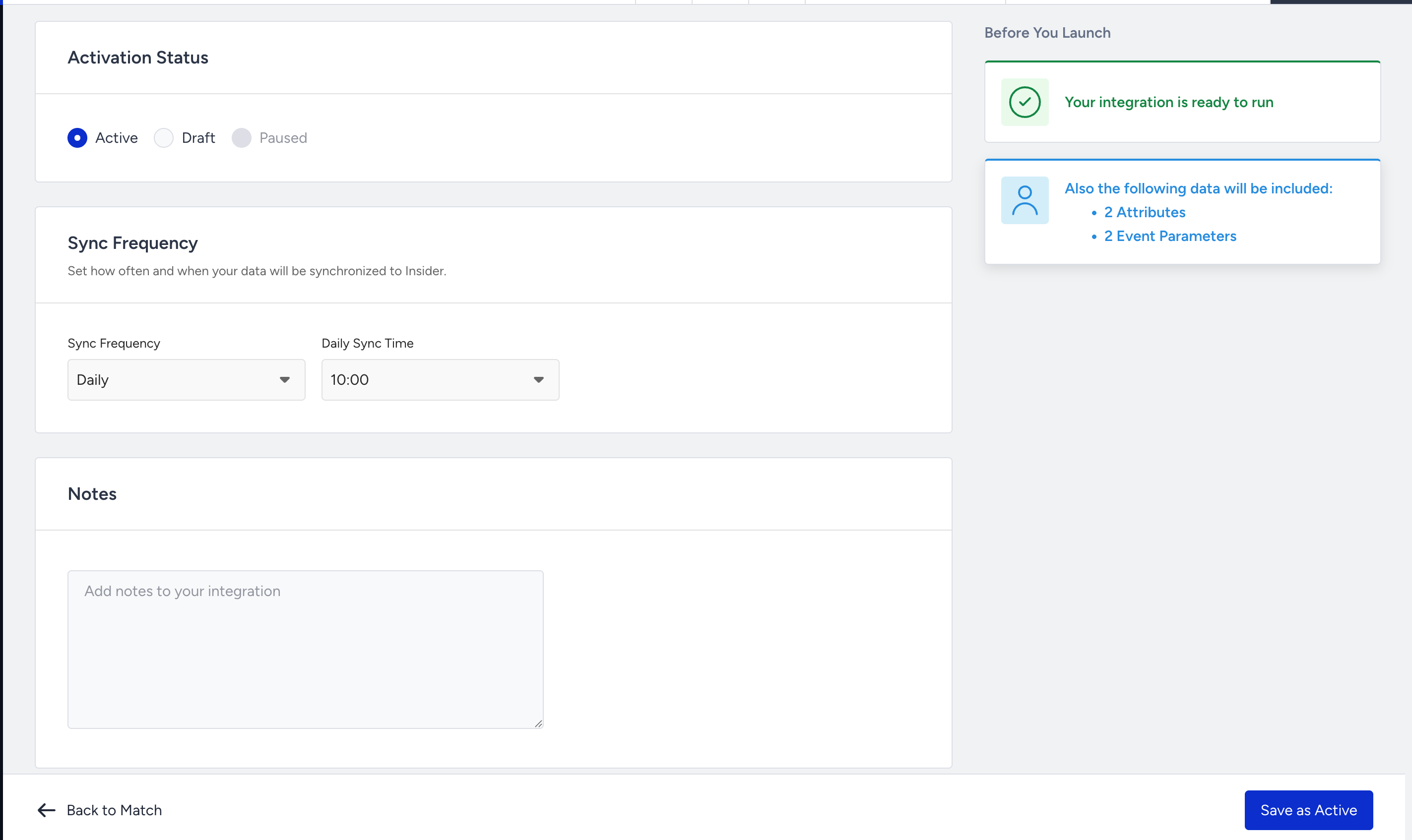
If the data volume on the BigQuery side exceeds 10 GB, Insider One cannot ingest the data in a single sync. To sync data over 10 GB, contact the Insider team.
Best Practices
Always use a dedicated service account with least-privilege access.
Ensure the Last Updated Column is reliably maintained to avoid unnecessary MTU usage and to retrieve the latest data.
Use BigQuery views to pre-filter or transform data before syncing.
Data Import Logic
During the GBQ → Insider synchronization:
If any identifier coming from GBQ is invalid, the entire record is not sent.
If an attribute coming from GBQ is invalid, only that specific attribute is skipped.
If an event parameter coming from GBQ is invalid, the entire event is excluded from processing.
The first synchronization performs a full table sync and doesn’t trigger any webhooks, campaigns, or journeys.
Important: Event Deduplication & Re-Ingestion Behavior
Duplicate Detection Rule: Insider One treats events with the same event name and timestamp as duplicates.
If multiple events with identical names and timestamps are sent within the same sync, only one will be processed and the others will be ignored.Avoid Updating Previously Synced Events: Do not update rows that were already consumed by Insider One in a previous sync.
Updating these rows triggers re-ingestion, which may create duplicate events in Insider.
Recommendation: Ensure each event has a unique timestamp and avoid modifying rows which include historical event records after they have been successfully synced.
Limitations
Each table must include an identifier.
Custom attributes or event parameters must be predefined in Insider One (via the Events & Attributes page).
For purchase events:
Add one row per product in a basket.
Include
e_guid(event_group_id) to link multiple rows to a single cart.
The synchronization process does not support
DELETEoperations. If a record is deleted from your GBQ table, the corresponding data will not be removed from Insider on the next sync.Each row (user) must be under 5 MB; rows exceeding this limit will not be upserted.
FAQ
Q: Can I use views as a source?
A: Yes, as long as the view is accessible by the service account and contains a Last Updated column.
Q: What happens if I delete a record in BigQuery?
A: Deletions are not propagated to Insider. Only new and updated records are synced.
Q: How do I add custom attributes or events?
A: Create them in Insider’s Events & Attributes page before mapping.
Q: What if my table does not have a Last Updated column?
A: The integration requires a Last Updated column for incremental sync. Please add one to your table or view, or your integration will stop data sync.